Phospholemman (FXYD1) associates with Na,K-ATPase and regulates its transport properties
- PMID: 12169672
- PMCID: PMC123281
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.182267299
Phospholemman (FXYD1) associates with Na,K-ATPase and regulates its transport properties
Abstract
A family of small, single-span membrane proteins (the FXYD family) has recently been defined based on their sequence and structural homology. Some members of this family have already been identified as tissue-specific regulators of Na,K-ATPase (NKA). In the present study, we demonstrate that phospholemman (PLM) (FXYD1), so far considered to be a heart- and muscle-specific channel or channel-regulating protein, associates specifically and stably with six different alpha-beta isozymes of NKA after coexpression in Xenopus oocytes, and with alpha1-beta, and less efficiently with alpha2-beta isozymes, in native cardiac and skeletal muscles. Stoichiometric association of PLM with NKA occurs posttranslationally either in the Golgi or the plasma membrane. Interaction of PLM with NKA induces a small decrease in the external K+ affinity of alpha1-beta1 and alpha2-beta1 isozymes and a nearly 2-fold decrease in the internal Na+ affinity. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that PLM is a tissue-specific regulator of NKA that may play an essential role in muscle contractility.
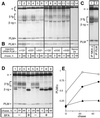
Figures



References
-
- Gheorghiade M. & Pitt, B. (1997) Am. Heart J. 134, 3-12. - PubMed
-
- Hamlyn J. M., Hamilton, B. P. & Manunta, P. (1996) J. Hypertens. 14, 151-167. - PubMed
-
- Geering K. (2001) J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 33, 425-438. - PubMed
-
- Crambert G., Hasler, U., Beggah, A. T., Yu, C., Modyanov, N. N., Horisberger, J. D., Lelièvre, L. & Geering, K. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 1976-1986. - PubMed
-
- Blanco G. & Mercer, R. W. (1998) Am. J. Physiol. 275, F633-F650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

