Randomized study of the benefits of preoperative corticosteroid administration on the postoperative morbidity and cytokine response in patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer
- PMID: 12170023
- PMCID: PMC1422564
- DOI: 10.1097/00000658-200208000-00006
Randomized study of the benefits of preoperative corticosteroid administration on the postoperative morbidity and cytokine response in patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether preoperative corticosteroid administration plays a role in attenuating postoperative morbidity.
Summary background data: There is as yet no consensus on the beneficial effects of steroids in alleviating surgical stress.
Methods: A total of 66 patients undergoing surgery for thoracic esophageal cancer were randomly categorized preoperatively into two groups of 33 patients each. One group was administered an intravenous infusion of methylprednisolone (10 mg/kg body weight) 30 minutes before the surgery (MP group), while the other group received a placebo infusion (control group). The primary endpoint was organ system failure during the first 7 days after surgery. Comparisons of surgery-related complications, cytokine responses, and blood counts were also made between the two groups.
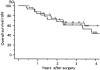
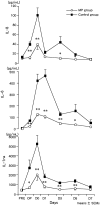
Results: The percentage of patients in the MP group who had one or more organ system failures was 33%, significantly lower than the corresponding percentage of 61% in the control group. The surgery-related complication rate and long-term survival rate were similar in the two groups. The peak plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist, IL-6, and IL-8 were significantly lower in the MP group than in the control group. Changes in the plasma levels of IL-10 were significantly larger in the MP group. No significant differences in the circulating lymphocyte and neutrophil counts were observed between the groups.
Conclusions: The results suggest that prophylactic administration of corticosteroids is associated with a decrease in postoperative morbidity in patients undergoing invasive surgery. The laboratory data suggest that corticosteroids may attenuate surgical stress-induced inflammatory responses both directly by suppressing the release of proinflammatory cytokines and via inducing IL-10 synthesis.
Figures


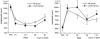
Comment in
-
The role of steroids in surgical practice.Curr Surg. 2003 May-Jun;60(3):235-40. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7944(03)00025-4. Curr Surg. 2003. PMID: 15212056 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sakamoto K, Arakawa H, Mita S, et al. Elevation of circulating interleukin-6 after surgery. Cytokine 1994; 6: 181–186. - PubMed
-
- Sato N, Murakami K, Ishida K, et al. Pulmonary hypertension and polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase after esophageal cancer operation. Ann Thorac Surg 1991; 51: 754–758. - PubMed
-
- Sato N, Koeda K, Kimura K, et al. Cytokine profile of serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids following thoracic esophageal cancer surgery. Eur Surg Res 2001; 33: 279–284. - PubMed
-
- Steven M. Confirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Crit Care Med 1997; 27: 1115–1123. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J, Carlet J. INTERSEPT. An international, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with sepsis. Crit Care Med 1996; 24: 1431–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

