Rescue of influenza B virus from eight plasmids
- PMID: 12172012
- PMCID: PMC123270
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.172393399
Rescue of influenza B virus from eight plasmids
Abstract
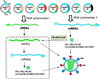
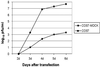
Influenza B virus causes a significant amount of morbidity and mortality, yet the systems to produce high yield inactivated vaccines for these viruses have lagged behind the development of those for influenza A virus. We have established a plasmid-only reverse genetics system for the generation of recombinant influenza B virus that facilitates the generation of vaccine viruses without the need for time consuming coinfection and selection procedures currently required to produce reassortants. We cloned the eight viral cDNAs of influenza B/Yamanashi/166/98, which yields relatively high titers in embryonated chicken eggs, between RNA polymerase I and RNA polymerase II transcription units. Virus was detected as early as 3 days after transfection of cocultured COS7 and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and achieved levels of 10(6)-10(7) plaque-forming units per ml of cell supernatant 6 days after transfection. The full-length sequence of the recombinant virus after passage into embryonated chicken eggs was identical to that of the input plasmids. To improve the utility of the eight-plasmid system for generating 6 + 2 reassortants from recently circulating influenza B strains, we optimized the reverse transcriptase-PCR for cloning of the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) segments. The six internal genes of B/Yamanashi/166/98 were used as the backbone to generate 6 + 2 reassortants including the HA and NA gene segments from B/Victoria/504/2000, B/Hong Kong/330/2001, and B/Hawaii/10/2001. Our results demonstrate that the eight-plasmid system can be used for the generation of high yields of influenza B virus vaccines expressing current HA and NA glycoproteins from either of the two lineages of influenza B virus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning of the canine RNA polymerase I promoter and establishment of reverse genetics for influenza A and B in MDCK cells.Virol J. 2007 Oct 23;4:102. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-102. Virol J. 2007. PMID: 17956624 Free PMC article.
-
Cloned cDNA of A/swine/Iowa/15/1930 internal genes as a candidate backbone for reverse genetics vaccine against influenza A viruses.Vaccine. 2012 Feb 14;30(8):1453-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.109. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 22230579 Free PMC article.
-
Development of high-yield influenza B virus vaccine viruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 20;113(51):E8296-E8305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616530113. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27930325 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse Genetics of Influenza B Viruses.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1602:205-238. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6964-7_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28508223
-
Eight-plasmid system for rapid generation of influenza virus vaccines.Vaccine. 2002 Aug 19;20(25-26):3165-70. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00268-2. Vaccine. 2002. PMID: 12163268
Cited by
-
Multiple gene segments control the temperature sensitivity and attenuation phenotypes of ca B/Ann Arbor/1/66.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(17):11014-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11014-11021.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16103152 Free PMC article.
-
Rescue of influenza C virus from recombinant DNA.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(20):11282-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00910-07. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17686850 Free PMC article.
-
Species specificity of the NS1 protein of influenza B virus: NS1 binds only human and non-human primate ubiquitin-like ISG15 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 12;285(11):7852-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C109.095703. Epub 2010 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20093371 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza B virus BM2 protein is transported through the trans-Golgi network as an integral membrane protein.J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(19):10630-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.19.10630-10637.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12970447 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterisation of influenza B viruses detected in Singapore, 2004 to 2009.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Dec 1;7:863. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-863. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25435177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klimov A., Simonsen, L., Fukuda, K. & Cox, N. (1999) Vaccine 17, Suppl. 1, S42-S46. - PubMed
-
- Rota P. A., Wallis, T. R., Harmon, M. W., Rota, J. S., Kendal, A. P. & Nerome, K. (1990) Virology 175, 59-68. - PubMed
-
- Rota P. A., Hemphill, M. L., Whistler, T., Regnery, H. L. & Kendal, A. P. (1992) J. Gen. Virol. 73, 2737-2742. - PubMed
-
- Nerome R., Hiromoto, Y., Sugita, S., Tanabe, N., Ishida, M., Matsumoto, M., Lindstrom, S. E., Takahashi, T. & Nerome, K. (1998) Arch. Virol. 143, 1569-1583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

