Cellular and subcellular localization of phototropin 1
- PMID: 12172018
- PMCID: PMC151461
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.003293
Cellular and subcellular localization of phototropin 1
Abstract
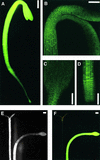
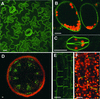
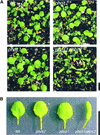
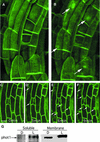
Phototropin 1 (phot1) is a Ser/Thr photoreceptor kinase that binds two molecules of flavin mononucleotide as its chromophores and undergoes autophosphorylation in response to blue light. Phot1 is plasma membrane associated and, as with phot2, has been shown to function as a photoreceptor for phototropism, blue light-induced chloroplast movement, and blue light-induced stomatal opening. Phot1 likely also plays a redundant role with phot2 in regulating the rate of leaf expansion. Understanding the mechanism(s) by which phot1 initiates these four different responses requires, at minimum, knowledge of where the photoreceptor is located. Therefore, we transformed a phot1 null mutant of Arabidopsis with a construct encoding translationally fused phot1-green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the control of the endogenous PHOT1 promoter and investigated its cellular and subcellular distribution. This PHOT1-GFP construct complements the mutant phenotype, restoring second positive curvature. Phot1 is expressed strongly in dividing and elongating cortical cells in the apical hook and in the root elongation zone in etiolated seedlings. It is localized evenly to the plasma membrane region in epidermal cells but is confined largely to the plasma membrane region of the transverse cell walls in the cortical cells of both root and hypocotyl. It is found at both apical and basal ends of these cortical cells. In light-grown plants, phot1-GFP is localized largely in the plasma membrane regions adjacent to apical and basal cell end walls in the elongating inflorescence stem, where the photoreceptor is expressed strongly in the vascular parenchyma and leaf vein parenchyma. Phot1 also is localized to the plasma membrane region of leaf epidermal cells, mesophyll cells, and guard cells, where its distribution is uniform. Although phot1 is localized consistently to the plasma membrane region in etiolated seedlings, a fraction becomes released to the cytoplasm in response to blue light. Possible relationships between observed phot1 distribution and the various physiological responses activated by blue light are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Assmann, S.M., Simoncini, L., and Schroeder, J.I. (1985). Blue light activates electrogenic ion pumping in guard cell protoplasts of Vicia faba. Nature 318, 285–287.
-
- Becraft, P.W. (1999). Development of the leaf epidermis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 45, 1–40. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, M.J., Marchant, A., Green, H.G., May, S.T., Ward, S.P., Nillner, P.A., Walker, A.R., Schulz, B., and Feldman, K.A. (1996). Arabidopsis AUX1 gene: A permease-like regulator of root gravitropism. Science 273, 948–950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

