Clinical short-term results of radiofrequency ablation in liver cancers
- PMID: 12174368
- PMCID: PMC4656310
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.624
Clinical short-term results of radiofrequency ablation in liver cancers
Abstract
Aim: To study local therapeutic efficacy, side effects, and complications of radiofrequency ablation (RFA), which is emerging as a new method for the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis and metastatic liver cancer.
Methods: Thirty-six patients with primary and secondary liver cancers (21 with primary hepatocellular carcinoma, 12 with colorectal cancer liver metastases and 3 with other malignant liver metastases), which were considered not suitable for curative resection, were include in this study. They were treated either with RFA (RITA2000, Mountain View, California, USA) percutaneously (n=20) or intraoperatively (n=16).The procedures were performed using the ultrasound guidance. The quality of RFA were based on monitoring of equipments and subject feeling of the practitioners. Patients treated with RFA was followed according to clinical findings,radiographic images, and tumor markers.
Results: Thirty-six patients underwent RFA for 48 nodules. RFA was used to treat an average 1.3 lesions per patient, and the median size of treated lesions was 2.5 cm (range, 0.5-9 cm). The average hospital stay was 5.6 days overall (2.8 days for percutaneous cases and 7.9 days for open operations). Seven patients underwent a second RFA procedure (sequential ablations). Sixteen HCC patients with a high level of alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and 9 colorectal cancer liver metastases patients with a high level of serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) have a great reduction benefited from RFA. Four (11.1 %) patients had complications: one skin burn; one postoperative hemorrhage; one cholecystitis and one hepatic abscess associated with percutaneous ablations of a large lesion. There were 4 deaths: 3 patients died from local and system diseases (1 at 7 month, 1 at 9 month, and 1 at 12 month), 1 patients died from cardiovascular shock, but no RFA-related death. At a median follow-up of 10 months (range, 1-24 months), 6 patients (16.7 %) had recurrences at an RFA site, and 20 patients (56.7 %) remained clinically free of disease.
Conclusion: RF ablation appears to be an effective, safe, and relatively simple procedure for the treatment of unresectable liver cancers. The rate and severity of complications appear acceptable. However, further study is necessary to assess combination with other therapies, long-term recurrence rates and effect on overall survival.
Figures
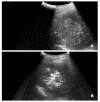
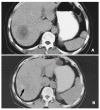
Comment in
-
Radiofrequency ablation: a good regional therapy for liver cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jan;9(1):192; author reply 192. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12572543 No abstract available.
References
-
- Weiss L, Grundmann E, Torhorst J, Hartveit F, Moberg I, Eder M, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Napier J, Horne CH, Lopez MJ. Haematogenous metastatic patterns in colonic carcinoma: an analysis of 1541 necropsies. J Pathol. 1986;150:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Nagorney DM, van Heerden JA, Ilstrup DM, Adson MA. Primary hepatic malignancy: surgical management and determinants of survival. Surgery. 1989;106:740–78; discussion 740-748;. - PubMed
-
- Fong Y, Cohen AM, Fortner JG, Enker WE, Turnbull AD, Coit DG, Marrero AM, Prasad M, Blumgart LH, Brennan MF. Liver resection for colorectal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:938–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

