Transforming growth factor-beta1 in invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 12174377
- PMCID: PMC4656319
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.674
Transforming growth factor-beta1 in invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the role of TGFbeta1 in invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer by analysing TGFbeta1 correlated with depth of tumor invasion, stage and metastasis.
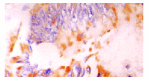
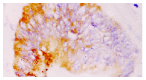
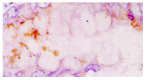
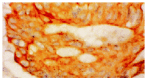
Methods: Serum TGFbeta1 levels were determined in 50 patients with colorectal cancer and 30 healthy volunteers using a TGFbeta1 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. TGFbeta1 expression in primary and lymph node metastatic lesions were detected in 98 cases of colorectal cancer by immunohistochemical staining and in situ hybridization.
Results: Serum levels of TGFbeta1 in patients with colorectal cancer(40+/-18 microg.L(-1)) were significantly higher than those in the healthy control group(19+/-8 microg.L(-1)), P<0.05. Elevated levels of serum TGFbeta1 were found in 60 % of patients with colorectal cancer when the mean +2 s was used as the upper limit of the normal range (35.1 microg.L(-1)). Increases in serum TGFbeta1 levels were significantly associated with Duke's stage (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference between Duke's stage B patients and Duke's stage C patients. In the cytoplasm of cancer cells, TGFbeta1 was immunostained in 37.8 % (37/98) of colorectal cancer, and this expression was confirmed by in situ hybridization. Among 35 cases of colorectal cancer with lymph node metastatic lesions, TGFbeta1 positive staining was found in 18 (51.4 %) cases of primary tumor, and 25 (71.4 %) cases with lymph node metastatic lesions, respectively. Of 17 cases w ith no staining in the primary lesion, 7 (41.2%) casesshowed TGFbeta1 staining in the metastatic lesion. Serum TGFbeta1 levels and TGFbeta1 expression in colorectal cancer tissues were correlated significantly with depth of tumor invasion, stage and metastasis. Patients in stage C-D,T3-T4 and with metastasis had significantly higher TGFbeta1 levels than patients in stage A-B,T1-T2 and without metastasis (P<0.05).
Conclusion: These results suggest that transforming growth factor-beta1 is closely related to the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. It increased the invasive and metastatic potential of tumor by altering a tumor microenvironment. TGFbeta1 may be used as a possible biomarker.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The angiogenic switch for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence during colorectal cancer progression.J Pathol. 2003 Jun;200(2):183-94. doi: 10.1002/path.1339. J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12754739
-
Role of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in invasion and metastasis in gastric carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 1999 Feb;17(2):607-14. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.2.607. J Clin Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10080606
-
Clinical significance of human erythrocyte glucose transporter 1 expression at the deepest invasive site of advanced colorectal carcinoma.Oncology. 2001;60(2):162-9. doi: 10.1159/000055314. Oncology. 2001. PMID: 11244332
-
TGFbeta1, back to the future: revisiting its role as a transforming growth factor.Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Mar;3(3):276-83. doi: 10.4161/cbt.3.3.849. Epub 2004 Mar 8. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15034302 Review.
-
Polysaccharide immunization and colorectal cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 22;9:961507. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.961507. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35938128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming growth factor beta 1 and metalloproteinase-9 overexpression in colorectal cancer (CC) and adenoma.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007 Oct;22(10):1165-72. doi: 10.1007/s00384-007-0296-9. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007. PMID: 17394006
-
A phase I dose-escalation study to a predefined dose of a transforming growth factor-β1 monoclonal antibody (TβM1) in patients with metastatic cancer.Int J Oncol. 2014 Dec;45(6):2221-31. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2679. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25270361 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Correlation of N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 overexpression with progressive growth of colorectal neoplasm.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Feb 15;10(4):550-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.550. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 14966915 Free PMC article.
-
In situ detection of TGF betas, TGF beta receptor II mRNA and telomerase activity in rat cholangiocarcinogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):590-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.590. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632524 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of N-(4-hydrophenyl) retinamide on liver cancer and malignant melanoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Oct 7;11(37):5763-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5763. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16270382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McEarchern JA, Kobie JJ, Mack V, Wu RS, Meade-Tollin L, Arteaga CL, Dumont N, Besselsen D, Seftor E, Hendrix MJ, et al. Invasion and metastasis of a mammary tumor involves TGF-beta signaling. Int J Cancer. 2001;91:76–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

