Anti-inflammatory effect of cholecystokinin and its signal transduction mechanism in endotoxic shock rat
- PMID: 12174384
- PMCID: PMC4656326
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.712
Anti-inflammatory effect of cholecystokinin and its signal transduction mechanism in endotoxic shock rat
Abstract
Aim: To study the anti-inflammatory effects of cholecystokinin-octapeptide (CCK-8) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock (ES) and further investigate its signal transduction pathways involving p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and IkappaB-alpha.
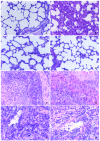
Methods: Eighty-four rats were divided randomly into four groups: LPS (8 mg.kg(-1), iv) induced ES; CCK-8 (40 microg.kg(-1), iv) pretreatment 10 min before LPS (8 mg.kg(-1)); CCK-8 (40 microg.kg(-1), iv) or normal saline (control) groups. The inflammatory changes of lung and spleen, phagocytic function of alveolar macrophage, quantification of inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) were investigated in rats by using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, phagocytosis of Candida albicans and differential cell counting. Nitric oxide (NO) production in serum, lung and spleen was measured with the Griess reaction. The mechanism involving p38 MAPK and IkappaB-alpha signal pathways was investigated by Western blot.
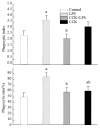
Results: Inflammatory changes of lung and spleen induced by LPS were alleviated by CCK-8, the increase of NO induced by LPS in serum, lung and spleen was significantly inhibited and the neutrophil infiltration in BAL was significantly reduced by CCK-8. The number of neutrophils was (52+/-10)X10(6) cells. (-1) in LPS group, while it decreased to (18+/-4)X10(6) cells. (-1) in CCK-8+LPS (P<0.01). The phagocytic rate of CCK-8 group increased to (62.49+/-9.49) %, compared with control group (48.16+/-14.20) %, P<0.05. The phagocytosis rate was (85.14+/-4.64) % in LPS group, which reduced to (59.33+/-3.14) % in CCK-8+LPS group (P<0.01). The results of phagocytosis indexes showed similar changes. CCK-8 may play an important role in increasing the expression of p38 MAPK and decreasing the degradation of IkappaB-alpha in lung and spleen of ES rats.
Conclusion: CCK-8 can result in anti-inflammatory effects, which may be related to activation of p38 MAPK and inhibition on the degradation of IkappaB-alpha.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCK-8 inhibits expression of TNF-alpha in the spleen of endotoxic shock rats and signal transduction mechanism of p38 MAPK.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Feb;8(1):139-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.139. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 11833090 Free PMC article.
-
[Inhibitory effect of cholecystokinin-octapeptide on production of cytokines in the lung of endotoxic shock rats].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2002 Apr 25;54(2):99-102. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2002. PMID: 11973585 Chinese.
-
Effect of cholecystokinin on cytokines during endotoxic shock in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Oct;7(5):667-71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.667. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819851 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects and mechanisms of cholecystokinin octapeptide on hippocampal injury during endotoxic shock].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2006 May;22(2):186-9. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 21162237 Chinese.
-
CCK-8 inhibits LPS-induced IL-1beta production in pulmonary interstitial macrophages by modulating PKA, p38, and NF-kappaB pathway.Shock. 2007 Jun;27(6):678-86. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e3180ze26dd. Shock. 2007. PMID: 17505309
Cited by
-
Cholecystokinin and the hormone concept.Endocr Connect. 2021 Mar;10(3):R139-R150. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0025. Endocr Connect. 2021. PMID: 33640870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of NF-kappaB and human telomerase reverse transcriptase in gastric cancer and precancerous lesions.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jan 15;10(2):177-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.177. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 14716817 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of a nerve injury transcriptional signature in airway-innervating sensory neurons after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):L953-L964. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00403.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32159971 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Peptides in Asthma-Obesity Phenotype.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 12;25(6):3213. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063213. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of CCK-8 and Cystathionine γ-Lyase/Hydrogen Sulfide System on Acute Lung Injury in Rats.Inflammation. 2017 Feb;40(1):174-183. doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0466-4. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 27882474
References
-
- Molina PE, Abumrad NN. Differential effects of hemorrhage and LPS on tissue TNF-alpha, IL-1 and associate neuro-hormonal and opioid alterations. Life Sci. 2000;66:399–409. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X, Demers LM. New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB, a ubiquitous transcription factor in the initiation of diseases. Clin Chem. 1999;45:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Kang JL, Lee K, Castranova V. Nitric oxide up-regulates DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor-kappaB in macrophages stimulated with silica and inflammatory stimulants. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000;215:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

