Hyposmotic membrane stretch potentiated muscarinic receptor agonist-induced depolarization of membrane potential in guinea-pig gastric myocytes
- PMID: 12174386
- PMCID: PMC4656328
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.724
Hyposmotic membrane stretch potentiated muscarinic receptor agonist-induced depolarization of membrane potential in guinea-pig gastric myocytes
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the relationship between hyposmotic membrane stretch and muscarinic receptor agonist-induced depolarization of membrane potential in antral gastric circular myocytes of guinea-pig.
Methods: Using whole cell patch-clamp technique recorded membrane potential and current in single gastric myocytes isolated by collagenase.
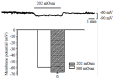
Results: Hyposmotic membrane stretch hyperpolarized membrane potential from -60.0mV+/-1.0mV to -67.9mV+/-1.0mV. TEA (10 mmol/L), a nonselective potassium channel blocker significantly inhibited hyposmotic membrane stretch-induced hyperpolarization. After KCl in the pipette and NaCl in the external solution were replaced by CsCl to block the potassium current, hyposmotic membrane stretch depolarized the membrane potential from -60.0 mV+/-1.0mV to -44.8 mV+/-2.3mV (P<0.05), and atropine (1 micromol/L) inhibited the depolarization of the membrane potential. Muscarinic receptor agonist Carbachol depolarized membrane potential from -60.0mV+/-1.0mV to -50.3 mV+/-0.3mV (P<0.05) and hyposmotic membrane stretch potentiated the depolarization. Carbachol induced muscarinic current (I( cch )) was greatly increased by hyposmotic membrane stretch.
Conclusion: Hyposmotic membrane stretch potentiated muscarinic receptor agonist-induced depolarization of membrane potential, which is related to hyposmotic membrane stretch-induced increase of muscarinic current.
Figures





References
-
- Coburn RF. Stretch-induced membrane depolarization in ferret trachealis smooth muscle cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987;62:2320–2325. - PubMed
-
- Harder DR. Pressure-dependent membrane depolarization in cat middle cerebral artery. Circ Res. 1984;55:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Harder DR, Gilbert R, Lombard JH. Vascular muscle cell depolarization and activation in renal arteries on elevation of transmural pressure. Am J Physiol. 1987;253:F778–F781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

