Kalirin Dbl-homology guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 domain initiates new axon outgrowths via RhoG-mediated mechanisms
- PMID: 12177196
- PMCID: PMC6757900
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-16-06980.2002
Kalirin Dbl-homology guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 domain initiates new axon outgrowths via RhoG-mediated mechanisms
Abstract
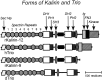
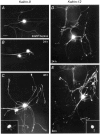
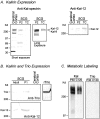
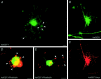
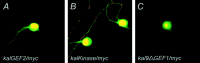
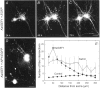
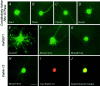
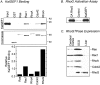
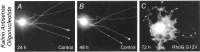
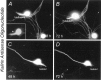
The large multidomain Kalirin and Trio proteins containing dual Rho GTPase guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) domains have been implicated in the regulation of neuronal fiber extension and pathfinding during development. In mammals, Kalirin is expressed predominantly in the nervous system, whereas Trio, broadly expressed throughout the body, is expressed at a lower level in the nervous system. To evaluate the role of Kalirin in fiber initiation and outgrowth, we microinjected cultured sympathetic neurons with vectors encoding Kalirin or with Kalirin antisense oligonucleotides, and we assessed neuronal fiber growth in a serum-free, satellite cell-free environment. Kalirin antisense oligonucleotides blocked the continued extension of preexisting axons. Kalirin overexpression induced the prolific sprouting of new axonal fibers that grew at the normal rate; the activity of Kalirin was entirely dependent on the activity of the first GEF domain. KalGEF1-induced sprouting of new fibers from lamellipodial structures was accompanied by extensive actin cytoskeleton reorganization. The kalGEF1 phenotype was mimicked by constitutively active RhoG and was blocked by RhoG inhibitors. Constitutively active Rac1, RhoA, and Cdc42 were unable to initiate new axons, whereas dominant-negative Rac1, RhoA, and Cdc42 failed to block axon sprouting. Thus Kalirin, acting via RhoG in a novel manner, plays a central role in establishing the morphological phenotypic diversity that is essential to the connectivity of the developing nervous system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct roles for the two Rho GDP/GTP exchange factor domains of kalirin in regulation of neurite growth and neuronal morphology.J Neurosci. 2001 Nov 1;21(21):8426-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08426.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11606631 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Rho-GEF trio and its target GTPase RhoG are involved in the NGF pathway, leading to neurite outgrowth.Curr Biol. 2002 Feb 19;12(4):307-12. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00658-9. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 11864571
-
An isoform of kalirin, a brain-specific GDP/GTP exchange factor, is enriched in the postsynaptic density fraction.J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6395-403. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.9.6395. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10692441
-
Kalirin: a dual Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor that is so much more than the sum of its many parts.Neuroscientist. 2005 Apr;11(2):148-60. doi: 10.1177/1073858404271250. Neuroscientist. 2005. PMID: 15746383 Review.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential activation and function of Rho GTPases during Salmonella-host cell interactions.J Cell Biol. 2006 Nov 6;175(3):453-63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605144. Epub 2006 Oct 30. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17074883 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the Rho/Rac family member RhoG in caveolar endocytosis.Oncogene. 2006 May 18;25(21):2961-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209333. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16568096 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cdk5 in Kalirin7-Mediated Formation of Dendritic Spines.Neurochem Res. 2019 May;44(5):1243-1251. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02771-y. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30875016
-
FE65 interacts with ADP-ribosylation factor 6 to promote neurite outgrowth.FASEB J. 2014 Jan;28(1):337-49. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-232694. Epub 2013 Sep 20. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24056087 Free PMC article.
-
The Guanine nucleotide exchange factor kalirin-7 is a novel synphilin-1 interacting protein and modifies synphilin-1 aggregate transport and formation.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051999. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23284848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acebes A, Ferrús A. Cellular and molecular features of axon collaterals and dendrites. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:557–565. - PubMed
-
- Alam MR, Caldwell BD, Johnson RC, Darlington DN, Mains RE, Eipper BA. Novel proteins that interact with the COOH-terminal cytosolic routing determinants of an integral membrane peptide-processing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28636–28640. - PubMed
-
- Alam MR, Johnson RC, Darlington DN, Hand TA, Mains RE, Eipper BA. Kalirin, a cytosolic protein with spectrin-like and GDP/GTP exchange factor-like domains that interacts with peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase, an integral membrane peptide-processing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:12667–12675. - PubMed
-
- Awasaki T, Saito M, Sone M, Suzuki E, Sakai R, Ito K, Hama C. The Drosophila Trio plays an essential role in patterning of axons by regulating their directional extension. Neuron. 2000;26:119–131. - PubMed
-
- Bateman J, Shu H, Van Vactor D. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Trio mediates axonal development in the Drosophila embryo. Neuron. 2000;26:93–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
