The non-Watson-Crick base pairs and their associated isostericity matrices
- PMID: 12177293
- PMCID: PMC134247
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf481
The non-Watson-Crick base pairs and their associated isostericity matrices
Abstract
RNA molecules exhibit complex structures in which a large fraction of the bases engage in non-Watson-Crick base pairing, forming motifs that mediate long-range RNA-RNA interactions and create binding sites for proteins and small molecule ligands. The rapidly growing number of three-dimensional RNA structures at atomic resolution requires that databases contain the annotation of such base pairs. An unambiguous and descriptive nomenclature was proposed recently in which RNA base pairs were classified by the base edges participating in the interaction (Watson-Crick, Hoogsteen/CH or sugar edge) and the orientation of the glycosidic bonds relative to the hydrogen bonds (cis or trans). Twelve basic geometric families were identified and all 12 have been observed in crystal structures. For each base pairing family, we present here the 4 x 4 'isostericity matrices' summarizing the geometric relationships between the 16 pairwise combinations of the four standard bases, A, C, G and U. Whenever available, a representative example of each observed base pair from X-ray crystal structures (3.0 A resolution or better) is provided or, otherwise, theoretically plausible models. This format makes apparent the recurrent geometric patterns that are observed and helps identify isosteric pairs that co-vary or interchange in sequences of homologous molecules while maintaining conserved three-dimensional motifs.
Figures











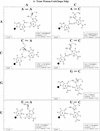







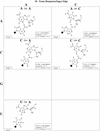





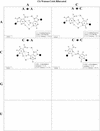

References
-
- Leontis N.B. and Westhof,E. (1998) A common motif organizes the structure of multi-helix loops in 16 S and 23 S ribosomal RNAs. J. Mol. Biol., 283, 571–583. - PubMed
-
- Moore P.B. (1999) Structural motifs in RNA. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 68, 287–300. - PubMed
-
- Hoogsteen K. (1963) The crystal and molecular structure of a hydrogen-bonded complex between 1-methylthymine and 9-methyladenine. Acta Crystallogr., 16, 907–916.

