Imprinting regulator DNMT3L is a transcriptional repressor associated with histone deacetylase activity
- PMID: 12177302
- PMCID: PMC134241
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf474
Imprinting regulator DNMT3L is a transcriptional repressor associated with histone deacetylase activity
Abstract
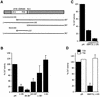
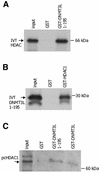
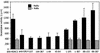
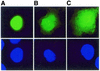
DNMT3L is a regulator of imprint establishment of normally methylated maternal genomic sequences. DNMT3L shows high similarity to the de novo DNA methyltransferases, DNMT3A and DNMT3B, however, the amino acid residues needed for DNA cytosine methyltransferase activity have been lost from the DNMT3L protein sequence. Apart from methyltransferase activity, Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b serve as transcriptional repressors associating with histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. Here we show that DNMT3L can also repress transcription by binding directly to HDAC1 protein. We have identified the PHD-like zinc finger of the ATRX domain as a main repression motif of DNMT3L, through which DNMT3L recruits the HDAC activity needed for transcriptional silencing. Furthermore, we show that DNMT3L protein contains an active nuclear localisation signal at amino acids 156-159. These results describe DNMT3L as a co-repressor protein and suggest that a transcriptionally repressed chromatin organisation through HDAC activity is needed for establishment of genomic imprints.
Figures
References
-
- Ferguson-Smith A.C. and Surani,M.A. (2001) Imprinting and the epigenetic asymmetry between parental genomes. Science, 293, 1086–1089. - PubMed
-
- Paulsen M. and Ferguson-Smith,A.C. (2001) DNA methylation in genomic imprinting, development and disease. J. Pathol., 95, 97–110. - PubMed
-
- Okano M., Bell,D.W., Haber,D.A. and Li,E. (1999) DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell, 99, 247–257. - PubMed
-
- Xu G.L., Bestor,T.H., Bourc’his,D., Hsieh,C.L., Tommerup,N., Bugge,M., Hulten,M., Qu,X., Russo,J.J. and Viegas-Pequignot,E. (1999) Chromosome instability and immunodeficiency syndrome caused by mutations in a DNA methyltransferase gene. Nature, 402, 187–191. - PubMed
-
- Amir R.E., Van den Veyver,I.B., Wan,M., Tran,C.Q., Francke,U. and Zoghbi,H.Y. (1999) Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nature Genet., 23, 185–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

