A functional gene discovery in the Fas-mediated pathway to apoptosis by analysis of transiently expressed randomized hybrid-ribozyme libraries
- PMID: 12177303
- PMCID: PMC134243
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf476
A functional gene discovery in the Fas-mediated pathway to apoptosis by analysis of transiently expressed randomized hybrid-ribozyme libraries
Abstract
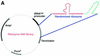
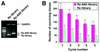
The sequence of much of the human genome is now available and the next goal is to identify functional genes and to clarify their roles. We have recently developed a novel system for isolation of genes in the Fas- and TNF-alpha-mediated pathways to apoptosis using poly(A)-connected hammerhead ribozyme libraries with randomized substrate-binding arms at both the 5' and 3' ends of ribozymes. The transcripts of these hybrid ribozymes have a poly(A) motif that can recruit RNA helicases and, thus, they can effectively attack target sites. In the previous studies, hybrid ribozymes were stably expressed. In order to save selection times, in this study we adopted transiently expressed hybrid ribozymes. In the case of Fas-mediated apoptosis, when we transiently introduced these hybrid-ribozyme libraries into Fas-expressing HeLa cells, we were able to isolate surviving clones that were resistant to or exhibited a delay in Fas-mediated apoptosis. We identified many pro-apoptotic genes and novel genes using this strategy with these transiently expressed hybrid-ribozyme libraries. In contrast, we identified significantly smaller numbers of candidate genes using conventional ribozyme libraries that were expressed transiently. Thus, when changes of a particular phenotype occur within a short period of time, our gene discovery system based on transiently expressed hybrid-ribozyme libraries should also be useful for the rapid identification of functional genes in the post-genome era.
Figures

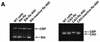
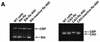

Similar articles
-
Identification of genes that function in the TNF-alpha-mediated apoptotic pathway using randomized hybrid ribozyme libraries.Nat Biotechnol. 2002 Apr;20(4):376-80. doi: 10.1038/nbt0402-376. Nat Biotechnol. 2002. Retraction in: Nat Biotechnol. 2006 Sep;24(9):1170. doi: 10.1038/nbt0906-1170e. PMID: 11923844 Retracted.
-
Mechanism of action of hammerhead ribozymes and their applications in vivo: rapid identification of functional genes in the post-genome era by novel hybrid ribozyme libraries.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Nov;30(Pt 6):1145-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0301145. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12440992 Review.
-
Discovery of functional genes in the post-genome era by novel RNA-protein hybrid ribozymes.Nucleic Acids Res Suppl. 2001;(1):133-4. doi: 10.1093/nass/1.1.133. Nucleic Acids Res Suppl. 2001. PMID: 12836300
-
A functional gene discovery in cell differentiation by hybrid ribozyme and siRNA libraries.Nucleic Acids Res Suppl. 2002;(2):275-6. doi: 10.1093/nass/2.1.275. Nucleic Acids Res Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12903211
-
Use of ribozymes in cellular aging research.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;371:209-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-361-5_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17634584 Review.
Cited by
-
Expressing functional siRNAs in mammalian cells using convergent transcription.BMC Biotechnol. 2003 Nov 6;3:21. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-3-21. BMC Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 14604435 Free PMC article.
-
Short hairpin type of dsRNAs that are controlled by tRNA(Val) promoter significantly induce RNAi-mediated gene silencing in the cytoplasm of human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 15;31(2):700-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg158. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12527779 Free PMC article.
-
The MUDENG Augmentation: A Genesis in Anti-Cancer Therapy?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 4;21(15):5583. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155583. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32759789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gintonin-Enriched Panax ginseng Extract Fraction Sensitizes Renal Carcinoma Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis through DR4/5 Upregulation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 27;46(10):10880-10895. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100646. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451526 Free PMC article.
-
Complete, gene-specific siRNA libraries: production and expression in mammalian cells.RNA. 2005 May;11(5):837-46. doi: 10.1261/rna.7285805. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15840823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lander E.S., Linton,L.M., Birren,B., Nusbaum,C., Zody,M.C., Baldwin,J., Devon,K., Dewar,K., Doyle,M., FitzHugh,W. et al. (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature, 409, 860–921. - PubMed
-
- Venter J.C., Adams,M.D., Myers,E.W., Li,P.W., Mural,R.J., Sutton,G.G., Smith,H.O., Yandell,M., Evans,C.A., Holt,R.A. et al. (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science, 291, 1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Trauth B.C., Klas,C., Peters,A.M., Matzku,S., Moller,P., Falk,W., Debatin,K.M. and Krammer,P.H. (1989) Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science, 245, 301–305. - PubMed
-
- Chinnaiyan A.M., O’Rourke,K., Tewari,M. and Dixit,V.M. (1995) FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell, 81, 505–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

