Counting CAG repeats in the Huntington's disease gene by restriction endonuclease EcoP15I cleavage
- PMID: 12177311
- PMCID: PMC134256
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnf082
Counting CAG repeats in the Huntington's disease gene by restriction endonuclease EcoP15I cleavage
Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with autosomal-dominant inheritance. The disease is caused by a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion located in the first exon of the HD gene. The CAG repeat is highly polymorphic and varies from 6 to 37 repeats on chromosomes of unaffected individuals and from more than 30 to 180 repeats on chromosomes of HD patients. In this study, we show that the number of CAG repeats in the HD gene can be determined by restriction of the DNA with the endonuclease EcoP15I and subsequent analysis of the restriction fragment pattern by electrophoresis through non-denaturing polyacrylamide gels using the ALFexpress DNA Analysis System. CAG repeat numbers in the normal (30 and 35 repeats) as well as in the pathological range (81 repeats) could be accurately counted using this assay. Our results suggest that this high-resolution method can be used for the exact length determination of CAG repeats in HD genes as well as in genes affected in related CAG repeat disorders.
Figures


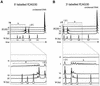

References
-
- Wanker E.E. (2000) Protein aggregation and pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease: mechanisms and correlations. Biol. Chem., 381, 937–942. - PubMed
-
- Gusella J.F. and MacDonald,M.E. (2000) Molecular genetics: unmasking polyglutamine triggers in neurodegenerative disease. Nature Rev. Neurosci., 1, 109–115. - PubMed
-
- Scherzinger E., Sittler,A., Schweiger,K., Heiser,V., Lurz,R., Hasenbank,R., Bates,G.P., Lehrach,H. and Wanker,E.E. (1999) Self-assembly of polyglutamine-containing huntingtin fragments into amyloid-like fibrils: implications for Huntington’s disease pathology. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 4604–4609. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

