Use of hybridization kinetics for differentiating specific from non-specific binding to oligonucleotide microarrays
- PMID: 12177314
- PMCID: PMC134259
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnf085
Use of hybridization kinetics for differentiating specific from non-specific binding to oligonucleotide microarrays
Abstract
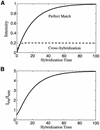
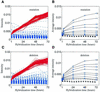
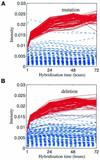
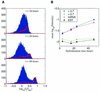
Hybridization kinetics were found to be significantly different for specific and non-specific binding of labeled cRNA to surface-bound oligonucleotides on microarrays. We show direct evidence that in a complex sample specific binding takes longer to reach hybridization equilibrium than the non- specific binding. We find that this property can be used to estimate and to correct for the hybridization contributed by non-specific binding. Useful applications are illustrated including the selection of superior oligonucleotides, and the reduction of false positives in exon identification.
Figures
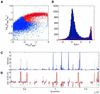
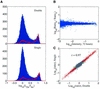
References
-
- Schena M., Shalon,D., Davis,R.W. and Brown,P.O. (1995) Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science, 270, 467–470. - PubMed
-
- Lockhart D.J., Dong,H., Byrne,M.C., Follettie,M.T., Gallo,M.V., Chee,M.S., Mittmann,M., Wang,C., Kobayashi,M., Horton,H. and Brown,E.L. (1996) Expression monitoring by hybridization to high-density oligo arrays. Nat. Biotechnol., 14, 1675–1680. - PubMed
-
- Lipshutz R.J., Fodor,S.P., Gingeras,T.R. and Lockhart,D.J. (1999) High density synthetic oligo arrays. Nature Genet., 21, 20–24. - PubMed
-
- Khan J., Wei,J.S., Ringner,M., Saal,L.H., Ladanyi,M., Westermann,F., Berthold,F., Schwab,M., Antonescu,C.R., Peterson,C. and Meltzer,P.S. (2001) Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks. Nature Med., 7, 777–888. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

