Up-regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism in tobacco cells constitutively expressing the human type I inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase
- PMID: 12177493
- PMCID: PMC166768
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.003426
Up-regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism in tobacco cells constitutively expressing the human type I inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase
Abstract
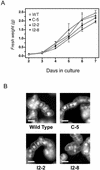
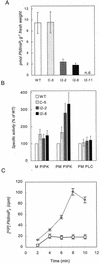
To evaluate the impact of suppressing inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP(3)) in plants, tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cells were transformed with the human type I inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (InsP 5-ptase), an enzyme which specifically hydrolyzes InsP(3). The transgenic cell lines showed a 12- to 25-fold increase in InsP 5-ptase activity in vitro and a 60% to 80% reduction in basal InsP(3) compared with wild-type cells. Stimulation with Mas-7, a synthetic analog of the wasp venom peptide mastoparan, resulted in an approximately 2-fold increase in InsP(3) in both wild-type and transgenic cells. However, even with stimulation, InsP(3) levels in the transgenic cells did not reach wild-type basal values, suggesting that InsP(3) signaling is compromised. Analysis of whole-cell lipids indicated that phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdInsP(2)), the lipid precursor of InsP(3), was greatly reduced in the transgenic cells. In vitro assays of enzymes involved in PtdInsP(2) metabolism showed that the activity of the PtdInsP(2)-hydrolyzing enzyme phospholipase C was not significantly altered in the transgenic cells. In contrast, the activity of the plasma membrane PtdInsP 5 kinase was increased by approximately 3-fold in the transgenic cells. In vivo labeling studies revealed a greater incorporation of (32)P into PtdInsP(2) in the transgenic cells compared with the wild type, indicating that the rate of PtdInsP(2) synthesis was increased. These studies show that the constitutive expression of the human type I InsP 5-ptase in tobacco cells leads to an up-regulation of the phosphoinositide pathway and highlight the importance of PtdInsP(2) synthesis as a regulatory step in this system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing the type 1 inositol 5-phosphatase exhibit increased drought tolerance and altered abscisic acid signaling.Plant Cell. 2008 Oct;20(10):2876-93. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.061374. Epub 2008 Oct 10. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18849493 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate affects the overall phosphoinositol pathway and leads to modifications in light signalling and secondary metabolism in tomato plants.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jan;63(2):825-35. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err306. Epub 2011 Oct 11. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 21994174 Free PMC article.
-
A universal role for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-mediated signaling in plant gravitropism.Plant Physiol. 2006 Feb;140(2):746-60. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.075119. Epub 2005 Dec 29. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16384898 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositide phosphatases: just as important as the kinases.Subcell Biochem. 2012;58:215-79. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-3012-0_7. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22403078 Review.
-
The role of the inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in cellular function and human disease.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 1;419(1):29-49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081673. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19272022 Review.
Cited by
-
Seed Biofortification and Phytic Acid Reduction: A Conflict of Interest for the Plant?Plants (Basel). 2015 Nov 20;4(4):728-55. doi: 10.3390/plants4040728. Plants (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27135349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing plasma membrane phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate biosynthesis increases phosphoinositide metabolism in Nicotiana tabacum.Plant Cell. 2007 May;19(5):1603-16. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.051367. Epub 2007 May 11. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17496116 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)bisphosphate inhibits K+-efflux channel activity in NT1 tobacco cultured cells.Plant Physiol. 2009 Feb;149(2):1127-40. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.129007. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19052153 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing the type 1 inositol 5-phosphatase exhibit increased drought tolerance and altered abscisic acid signaling.Plant Cell. 2008 Oct;20(10):2876-93. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.061374. Epub 2008 Oct 10. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18849493 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate biosynthesis affects plant nuclear lipids and nuclear functions.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012 Aug;57:32-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.05.011. Epub 2012 May 17. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22677448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aducci P, Marra M. IP3 levels and their modulation by fusicoccin measured by a novel [3H] IP3 binding assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;168:1041–1046. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signaling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Brearley CA, Hanke DE. Metabolic relations of inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate revealed by cell permeabilization. Identification of inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase and inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate phosphatase activities in mesophyll cells. Plant Physiol. 2000;122:1209–1216. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

