Cadmium-induced sulfate uptake in maize roots
- PMID: 12177501
- PMCID: PMC166776
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.002659
Cadmium-induced sulfate uptake in maize roots
Abstract
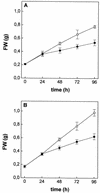
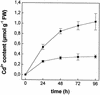
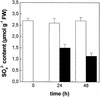
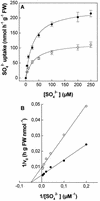
The effect of cadmium (Cd) on high-affinity sulfate transport of maize (Zea mays) roots was studied and related to the changes in the levels of sulfate and nonprotein thiols during Cd-induced phytochelatin (PC) biosynthesis. Ten micromolar CdCl(2) in the nutrient solution induced a 100% increase in sulfate uptake by roots. This was not observed either for potassium or phosphate uptake, suggesting a specific effect of Cd(2+) on sulfate transport. The higher sulfate uptake was not dependent on a change in the proton motive force that energizes it. In fact, in Cd-treated plants, the transmembrane electric potential difference of root cortical cells was only slightly more negative than in the controls, the external pH did not change, and the activity of the plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase did not increase. Kinetics analysis showed that in the range of the high-affinity sulfate transport systems, 10 to 250 microM, Cd exposure did not influence the K(m) value (about 20 microM), whereas it doubled the V(max) value with respect to the control. Northern-blot analysis showed that Cd-induced sulfate uptake was related to a higher level of mRNA encoding for a putative high-affinity sulfate transporter in roots. Cd-induced sulfate uptake was associated to both a decrease in the contents of sulfate and glutathione and synthesis of a large amount of PCs. These results suggest that Cd-induced sulfate uptake depends on a pretranslational regulation of the high-affinity sulfate transporter gene and that this response is necessary for sustaining the higher sulfur demand during PC biosynthesis.
Figures
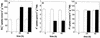

Similar articles
-
Cadmium inhibits the induction of high-affinity nitrate uptake in maize (Zea mays L.) roots.Planta. 2012 Dec;236(6):1701-12. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1729-4. Epub 2012 Aug 5. Planta. 2012. PMID: 22983671
-
Heavy metal stress and sulfate uptake in maize roots.Plant Physiol. 2006 Jul;141(3):1138-48. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.076240. Epub 2006 May 12. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16698905 Free PMC article.
-
Chromate differentially affects the expression of a high-affinity sulfate transporter and isoforms of components of the sulfate assimilatory pathway in Zea mays (L.).Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2007 Sep;9(5):662-71. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-965440. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2007. PMID: 17853366
-
Effects of Cadmium Treatment on the Uptake and Translocation of Sulfate in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2016 Nov;57(11):2353-2366. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw156. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27590710
-
Molecular mechanisms of phosphate and sulphate transport in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 1;1465(1-2):236-45. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00141-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10748257 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of sulfur and cadmium on antioxidants, phytochelatins and growth in Indian mustard.AoB Plants. 2015 Jan 12;7:plv001. doi: 10.1093/aobpla/plv001. AoB Plants. 2015. PMID: 25587194 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of cadmium with glutathione and photosynthesis in developing leaves and chloroplasts of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steudel.Plant Physiol. 2003 Oct;133(2):829-37. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.026518. Epub 2003 Oct 2. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14526113 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hg, As and Pb on biomass production, photosynthetic rate, nutrients uptake and phytochelatin induction in Pfaffia glomerata.Ecotoxicology. 2013 Nov;22(9):1403-12. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1126-1. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Ecotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 24068651
-
Impact of copper oxide nanoparticles exposure on Arabidopsis thaliana growth, root system development, root lignificaion, and molecular level changes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014 Nov;21(22):12709-22. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3210-3. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24965006
-
Phytochelatins: Sulfur-Containing Metal(loid)-Chelating Ligands in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2430. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032430. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bolchi A, Petrucco S, Tenca PL, Foroni C, Ottonello S. Coordinate modulation of maize sulfate permease and ATP sulfurylase mRNAs in response to variations in sulfur nutritional status: stereospecific down-regulation by l-cysteine. Plant Mol Biol. 1999;39:527–537. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Clarkson DT, Smith FW, Vanden Berg PJ. Regulation of sulphate transport in tropical legume, Macroptilum atropurpureum, cv. Siratro J Exp Bot. 1983;34:1463–1483.
-
- Clemens S. Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta. 2001;212:475–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

