The antitumour activity of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) in TNF receptor-1 knockout mice
- PMID: 12177785
- PMCID: PMC2376130
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600479
The antitumour activity of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) in TNF receptor-1 knockout mice
Abstract
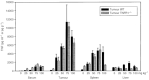
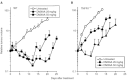
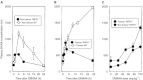
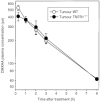
5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid, a novel antivascular anticancer drug, has completed Phase I clinical trial. Its actions in mice include tumour necrosis factor induction, serotonin release, tumour blood flow inhibition, and the induction of tumour haemorrhagic necrosis and regression. We have used mice with a targeted disruption of the tumour necrosis factor receptor-1 gene as recipients for the colon 38 carcinoma to determine the role of tumour necrosis factor signalling in the action of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid. The pharmacokinetics of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid, as well as the degree of induced plasma and tissue tumour necrosis factor, were similar in tumour necrosis factor receptor-1(-/-) and wild-type mice. However, the maximum tolerated dose of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid was considerably higher in tumour necrosis factor receptor-1(-/-) mice (>100 mg kg(-1)) than in wild-type mice (27.5 mg kg(-1)). The antitumour activity of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (25 mg kg(-1)) was strongly attenuated in tumour necrosis factor receptor-1(-/-) mice. However, the reduced toxicity in tumour necrosis factor receptor-1(-/-) mice allowed the demonstration that at a higher dose (50 mg kg(-1)), 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid was curative and comparable in effect to that of a lower dose (25 mg kg(-1)) in wild-type mice. The 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid -induced rise in plasma 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, used to reflect serotonin production in a vascular response, was larger in colon 38 tumour bearing than in non-tumour bearing tumour necrosis factor receptor-1(-/-) mice, but in each case the response was smaller than the corresponding response in wild-type mice. The results suggest an important role for tumour necrosis factor in mediating both the host toxicity and antitumour activity of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid, but also suggest that tumour necrosis factor can be replaced by other vasoactive factors in its antitumour action, an observation of relevance to current clinical studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral activity and pharmacokinetics of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) in mice.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;49(1):20-6. doi: 10.1007/s00280-001-0377-3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11855749
-
Effects of the serotonin receptor antagonist cyproheptadine on the activity and pharmacokinetics of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA).Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;47(6):491-7. doi: 10.1007/s002800000267. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11459201
-
DMXAA: an antivascular agent with multiple host responses.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002 Dec 1;54(5):1503-11. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)03920-2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. PMID: 12459378
-
5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA): a new biological response modifier for cancer therapy.Invest New Drugs. 2002 Aug;20(3):281-95. doi: 10.1023/a:1016215015530. Invest New Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12201491 Review.
-
Antivascular therapy of cancer: DMXAA.Lancet Oncol. 2003 Mar;4(3):141-8. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(03)01018-0. Lancet Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12623359 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct Activation of STING in the Tumor Microenvironment Leads to Potent and Systemic Tumor Regression and Immunity.Cell Rep. 2015 May 19;11(7):1018-30. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.031. Epub 2015 May 7. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25959818 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological Role of Nucleic Acid-Sensing Pattern Recognition Receptors in Inflammatory Diseases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 6;12:910654. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.910654. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35734577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DMXAA causes tumor site-specific vascular disruption in murine non-small cell lung cancer, and like the endogenous non-canonical cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist, 2'3'-cGAMP, induces M2 macrophage repolarization.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 18;9(6):e99988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099988. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24940883 Free PMC article.
-
Effects on Metabolism in Astrocytes Caused by cGAMP, Which Imitates the Initial Stage of Brain Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 21;22(16):9028. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169028. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445736 Free PMC article.
-
Aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy combined with topically applied vascular disrupting agent vadimezan leads to enhanced antitumor responses.Photochem Photobiol. 2011 Jul-Aug;87(4):910-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2011.00943.x. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Photochem Photobiol. 2011. PMID: 21575001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AggarwalBBNatarajanK1996Tumour necrosis factors: developments during the last decade Eur Cytokine Netw 793124 - PubMed
-
- BaguleyBC2001Small-molecule cytokine inducers causing tumor necrosis Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2967975 - PubMed
-
- BaguleyBCCalveleySBCroweKKFrayLMO'RourkeSASmithGP1989Comparison of the effects of flavone acetic acid, fostriecin, homoharringtonine and tumour necrosis factor alpha on Colon 38 tumors in mice Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 25263269 - PubMed
-
- BaguleyBCColeGThomsenLLZhuangL1993Serotonin involvement in the antitumour and host effects of flavone-8-acetic acid and 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 337781 - PubMed
-
- BaguleyBCZhuangLKestellP1997Increased plasma serotonin following treatment with flavone-8-acetic acid, 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid, vinblastine, and colchicine - relation to vascular effects Oncol Res 95560 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

