A comparison of cognitive-processing therapy with prolonged exposure and a waiting condition for the treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder in female rape victims
- PMID: 12182270
- PMCID: PMC2977927
- DOI: 10.1037//0022-006x.70.4.867
A comparison of cognitive-processing therapy with prolonged exposure and a waiting condition for the treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder in female rape victims
Abstract
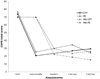
The purpose of this study was to compare cognitive-processing therapy (CPT) with prolonged exposure and a minimal attention condition (MA) for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and depression. One hundred seventy-one female rape victims were randomized into 1 of the 3 conditions, and 121 completed treatment. Participants were assessed with the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale, the PTSD Symptom Scale, the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV, the Beck Depression Inventory, and the Trauma-Related Guilt Inventory. Independent assessments were made at pretreatment, posttreatment, and 3 and 9 months posttreatment. Analyses indicated that both treatments were highly efficacious and superior to MA. The 2 therapies had similar results except that CPT produced better scores on 2 of 4 guilt subscales.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Atkeson BM, Calhoun KS, Resick PA, Ellis EM. Victims of rape: Repeated assessment of depressive symptoms. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1982;50:96–102. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Garbin MG. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: Twenty-five years of evaluation. Clinical Psychology Review. 1988;8:77–100.
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelsohn M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1961;4:561–571. - PubMed
-
- Blake DD, Weathers FW, Nagy LM, Kaloupek DG, Gusman FD, Charney DS, Keane TM. The development of a clinician-administered PTSD scale. Journal of Traumatic Stress. 1995;8:75–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

