Importance of the fourth alpha-helix within the CAP homology domain of type II topoisomerase for DNA cleavage site recognition and quinolone action
- PMID: 12183223
- PMCID: PMC127396
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.9.2735-2746.2002
Importance of the fourth alpha-helix within the CAP homology domain of type II topoisomerase for DNA cleavage site recognition and quinolone action
Abstract
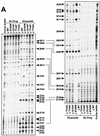
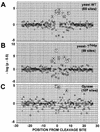
We report that point mutations causing alteration of the fourth alpha-helix (alpha4-helix) of the CAP homology domain of eukaryotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) type II topoisomerases (Ser(740)Trp, Gln(743)Pro, and Thr(744)Pro) change the selection of type II topoisomerase-mediated DNA cleavage sites promoted by Ca(2+) or produced by etoposide, the fluoroquinolone CP-115,953, or mitoxantrone. By contrast, Thr(744)Ala substitution had minimal effect on Ca(2+)- and drug-stimulated DNA cleavage sites, indicating the selectivity of single amino acid substitutions within the alpha4-helix on type II topoisomerase-mediated DNA cleavage. The equivalent mutation in the gene for Escherichia coli gyrase causing Ser(83)Trp also changed the DNA cleavage pattern generated by Ca(2+) or quinolones. Finally, Thr(744)Pro substitution in the yeast type II topoisomerase rendered the enzyme sensitive to antibacterial quinolones. This study shows that the alpha4-helix within the conserved CAP homology domain of type II topoisomerases is critical for selecting the sites of DNA cleavage. It also demonstrates that selective amino acid residues in the alpha4-helix are important in determining the activity and possibly the binding of quinolones to the topoisomerase II-DNA complexes.
Figures


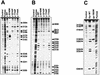




Similar articles
-
A mutation in yeast TOP2 homologous to a quinolone-resistant mutation in bacteria. Mutation of the amino acid homologous to Ser83 of Escherichia coli gyrA alters sensitivity to eukaryotic topoisomerase inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20359-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20359. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7657608
-
A mutation in Escherichia coli DNA gyrase conferring quinolone resistance results in sensitivity to drugs targeting eukaryotic topoisomerase II.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Dec;48(12):4495-504. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4495-4504.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15561817 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavable-complex formation by wild-type and quinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae type II topoisomerases mediated by gemifloxacin and other fluoroquinolones.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Feb;46(2):413-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.2.413-419.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11796351 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of action of the new quinolones: new data.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;10(4):223-31. doi: 10.1007/BF01966994. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991. PMID: 1650698 Review.
-
Bacterial topoisomerases, anti-topoisomerases, and anti-topoisomerase resistance.Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Aug;27 Suppl 1:S54-63. doi: 10.1086/514923. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. PMID: 9710672 Review.
Cited by
-
The alpha4 residues of human DNA topoisomerase IIalpha function in enzymatic activity and anticancer drug sensitivity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Mar 16;32(5):1767-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh339. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15026536 Free PMC article.
-
Smoothed Potential MD Simulations for Dissociation Kinetics of Etoposide To Unravel Isoform Specificity in Targeting Human Topoisomerase II.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Sep 23;59(9):4007-4017. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00605. Epub 2019 Sep 9. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31449404 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling between ATP binding and DNA cleavage by DNA topoisomerase II: A unifying kinetic and structural mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 20;283(25):17463-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710014200. Epub 2008 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18403371 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in resistant mutants of Clostridium perfringens found after in vitro treatment with fluoroquinolones.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Feb;49(2):488-92. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.2.488-492.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15673722 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing sensitivity to antibacterial topoisomerase II inhibitors.Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;Chapter 3:Unit3.13. doi: 10.1002/0471141755.ph0313s39. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 21948169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, V. E., T. D. Gootz, and N. Osheroff. 1998. Topoisomerase IV catalysis and the mechanism of quinolone action. J. Biol. Chem. 273:17879-17885. - PubMed
-
- Andoh, T., and R. Ishida. 1998. Catalytic inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1400:155-171. - PubMed
-
- Beck, W. T., M. K. Danks, J. S. Wolverton, R. Kim, and M. Chen. 1993. Drug resistance associated with altered DNA topoisomerase II. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 33:113-127. - PubMed
-
- Berger, J. 1998. Type II DNA topoisomerases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8:26-32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

