Immunomodulatory effect of zidovudine (ZDV) on cytotoxic T lymphocytes previously exposed to ZDV
- PMID: 12183239
- PMCID: PMC127449
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.9.2865-2871.2002
Immunomodulatory effect of zidovudine (ZDV) on cytotoxic T lymphocytes previously exposed to ZDV
Abstract
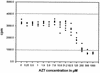
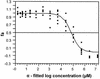
In a previous study, zidovudine (ZDV) was shown to cause a concentration-dependent inhibition of antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) clonal expansion (S. Francke, C. G. Orosz, K. A. Hayes, and L. E. Mathes, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:1900-1905, 2000). However, this suppressive effect was lost if exposure to ZDV was delayed for 24 to 48 h during the antigen sensitization period, suggesting that antigen-primed CTL may be less susceptible than naive T lymphocytes to the suppressive effects of ZDV. The present study was undertaken to determine if naive T lymphocytes were more sensitive to the suppressive effects of ZDV than T lymphocytes previously exposed to antigen. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) values of ZDV were determined on naive and antigen-primed T-cell responses in an alloantigen system. Lymphocyte cultures with continuous antigen exposure (double prime) were more resistant to ZDV suppression (IC(50) = 316 micro M) than were naive lymphocytes (IC(50) = 87.5 micro M). Interestingly, lymphocytes that were antigen primed but deprived of antigen during the final 7 days of culture (prime/hold) were exquisitely sensitive to ZDV suppression (IC(50) = 29.3 micro M). The addition of 80 micro M ZDV during the initial priming of the single-prime (prime/hold) and double-prime cultures did not select for a more drug-resistant cell population. The differences in ZDV sensitivities are likely a reflection of the physiological properties of the lymphocytes related to their activation state.
Figures
References
-
- Andrew, M. E., V. L. Braciale, and T. J. Braciale. 1984. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression on murine cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones. J. Immunol. 132:839-844. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli, G., O. Turriziani, M. Cianfriglia, E. Riva, G. Dong, A. Fattorossi, and F. Dianzani. 1992. Resistance of HIV-1 to AZT might also involve the cellular expression of multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 8:1839-1844. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli, G., O. Turriziani, A. Verri, P. Narciso, F. Ferri, G. D'Offizi, and F. Dianzani. 1996. Long-term exposure to zidovudine affects in vitro and in vivo the efficiency of phosphorylation of thymidine kinase. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 12:223-228. - PubMed
-
- Arts, E. J., and M. A. Wainberg. 1996. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase and early events in reverse transcription. Adv. Virus Res. 46:97-163. - PubMed
-
- Avramis, V. I., R. Kwock, M. M. Solorzano, and E. Gomperts. 1993. Evidence of in vitro development of drug resistance to azidothymidine in T-lymphocytic leukemia cell lines (Jurkat E6-1/AZT-100) and in pediatric patients with HIV-1 infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 6:1287-1296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

