Phase I dose escalation trial evaluating the pharmacokinetics, anti-human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) activity, and safety of 1263W94 in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men with asymptomatic HCMV shedding
- PMID: 12183255
- PMCID: PMC127448
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.9.2969-2976.2002
Phase I dose escalation trial evaluating the pharmacokinetics, anti-human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) activity, and safety of 1263W94 in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men with asymptomatic HCMV shedding
Abstract
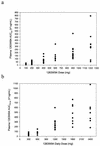
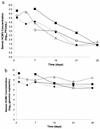
1263W94 [maribavir; 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1,beta-L-ribofuranosyl-1-H-benzimidazole] is a novel benzimidazole compound for treatment of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection and disease, with potent in vitro activity against HCMV and good oral bioavailability. A phase I study was conducted to determine the pharmacokinetics (PK), anti-HCMV activity, and safety of 1263W94 administered as multiple oral doses to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected adult male subjects with asymptomatic HCMV shedding. Subjects received one of six dosage regimens (100, 200, or 400 mg three times a day, or 600, 900, or 1,200 mg twice a day) or a placebo for 28 days. 1263W94 demonstrated linear PK, with steady-state plasma 1263W94 profiles predictable based on single-dose data. 1263W94 was rapidly absorbed following oral dosing, and values for the maximum concentration of the drug in plasma and the area under the concentration-time curve increased in proportion to the dose. 1263W94 demonstrated in vivo anti-HCMV activity in semen at all of the dosage regimens tested, with mean reductions in semen HCMV titers of 2.9 to 3.7 log(10) PFU/ml among the four regimens evaluated for anti-HCMV activity. 1263W94 was generally well tolerated; taste disturbance was the most frequently reported adverse event over the 28-day dosing period.
Figures
References
-
- Biron, K., S. Chamberlain, R. Harvey, S. Good, A. Smith, M. Davis, C. Talarico, W. Miller, R. Ferris, R. Dornsife, S. Stanat, J. Drach, L. Townsend, and G. Koszalka. Potent and selective inhibition of human cytomegalovirus replication by 1263W94, a benzimidazole l-riboside with a unique mode of action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother., in press. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cherrington, J., R. Miner, M. Hitchcock, J. Lalezari, and W. Drew. 1996. Susceptibility of human cytomegalovirus to cidofovir is unchanged after limited in vivo exposure to various regimens of drug. J. Infect. Dis. 173:987-992. - PubMed
-
- Chulay, J., K. Biron, L. Want, M. Underwood, S. Chamberlain, L. Frick, S. Good, M. Davis, R. Harvey, L. Townsend, J. Drach, and G. Koszalka. 1999. Development of novel benzimdazole riboside compounds for treatment of cytomegalovirus disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 458:129-134. - PubMed
-
- Drew, W., R. Miner, D. Busch, S. Follansbee, J. Gullet, S. Mehalko, S. Gordon, W. Owen, T. Matthew, W. Buhles, et al. 1991. Prevalence of resistance in patients receiving ganciclovir for serious cytomegalovirus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 163:716-719. - PubMed
-
- Drew, W., R. Miner, and E. Saleh. 1993. Antiviral testing of cytomegalovirus: criteria for detecting resistance to antivirals. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1:179-195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

