Efficacy of handrubbing with alcohol based solution versus standard handwashing with antiseptic soap: randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 12183307
- PMCID: PMC117885
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.325.7360.362
Efficacy of handrubbing with alcohol based solution versus standard handwashing with antiseptic soap: randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy of handrubbing with an alcohol based solution versus conventional handwashing with antiseptic soap in reducing hand contamination during routine patient care.
Design: Randomised controlled trial during daily nursing sessions of 2 to 3 hours.
Setting: Three intensive care units in a French university hospital.
Participants: 23 healthcare workers.
Interventions: Handrubbing with alcohol based solution (n=12) or handwashing with antiseptic soap (n=11) when hand hygiene was indicated before and after patient care. Imprints taken of fingertips and palm of dominant hand before and after hand hygiene procedure. Bacterial counts quantified blindly.
Main outcome measures: Bacterial reduction of hand contamination.
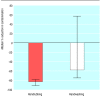
Results: With handrubbing the median percentage reduction in bacterial contamination was significantly higher than with handwashing (83% v 58%, P=0.012), with a median difference in the percentage reduction of 26% (95% confidence interval 8% to 44%). The median duration of hand hygiene was 30 seconds in each group.
Conclusions: During routine patient care handrubbing with an alcohol based solution is significantly more efficient in reducing hand contamination than handwashing with antiseptic soap.
Figures
Comment in
-
Alcohol handrubs v soap. Finnish experience shows that alcohol rubs are good for hands.BMJ. 2003 Jan 4;326(7379):50. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7379.50/a. BMJ. 2003. PMID: 12511470 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alcohol handrubs v soap. Alcohol handrub removes methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus.BMJ. 2003 Jan 4;326(7379):50. BMJ. 2003. PMID: 12518767 No abstract available.
-
Handrubbing with an alcohol based solution reduced healthcare workers' hand contamination more than handwashing with antiseptic soap.Evid Based Nurs. 2003 Apr;6(2):54-5. Evid Based Nurs. 2003. PMID: 12710429 No abstract available.
References
-
- Conly JM, Hill S, Ross J, Lertzman J, Louie TJ. Handwashing practices in an intensive care unit: the effects of an educational program and its relationship to infection rates. Am J Infect Control. 1989;17:330–339. - PubMed
-
- Pittet D, Mourouga P, Perneger TV the Members of the Infection Control Program. Compliance with handwashing in a teaching hospital. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:126–130. - PubMed
-
- Rotter ML. Hand washing, hand disinfection and skin disinfection. In: Mayhall G, editor. Hospital epidemiology and infection control. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; 1999. pp. 691–709.
-
- Preston GA, Larson EL, Stamm WE. The effect of private isolation rooms on patient care practices, colonization and infection in an intensive care unit. Am J Med. 1981;70:641–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
