Subversion of cell signaling pathways by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein via interaction with Grb2 and P85 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PMID: 12186904
- PMCID: PMC136456
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9207-9217.2002
Subversion of cell signaling pathways by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein via interaction with Grb2 and P85 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
Abstract
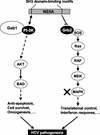
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) sets up a persistent infection in patients that likely involves a complex virus-host interaction. We previously found that the HCV nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein interacts with growth factor receptor-binding protein 2 (Grb2) adaptor protein and inhibits the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) by epidermal growth factor (EGF). In the present study, we extended this analysis and investigated the specificity of the Grb2-NS5A interaction and whether the subversion of mitogenic signaling involves additional pathways. NS5A containing mutations within the C-terminal proline-rich motif neither bound Grb2 nor inhibited ERK1/2 activation by EGF, demonstrating that NS5A-Grb2 binding and downstream effects were due to direct interactions. Interestingly, NS5A could also form a complex with the Grb2-associated binder 1 (Gab1) protein in an EGF treatment-dependent manner. However, the NS5A-Gab1 association, which appeared indirect, was not mediated by direct NS5A-Grb2 interaction but was likely dependent on direct NS5A interaction with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). The in vivo association of NS5A with p85 PI3K required the N-terminal, but not the C-terminal, region of NS5A. The downstream effects of the NS5A-p85 PI3K interaction included increased tyrosine phosphorylation of p85 PI3K in response to EGF. Consistent with this observation and the antiapoptotic properties of NS5A, we also detected enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of the downstream AKT protein kinase and increased serine phosphorylation of BAD, a proapoptotic factor and an AKT substrate, in the presence of NS5A. These results collectively suggest a model in which NS5A interacts with Grb2 to inhibit mitogenic signaling while simultaneously promoting the PI3K-AKT cell survival pathway by interaction with p85 PI3K, which may represent a crucial step in HCV persistence and pathogenesis.
Figures

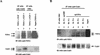


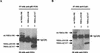

References
-
- Aizaki, H., S. Saito, T. Ogino, N. Miyajima, T. Harada, Y. Matsuura, T. Miyamura, and M. Kohase. 2000. Suppression of interferon-induced antiviral activity in cells expressing hepatitis C virus proteins. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 20:1111-1120. - PubMed
-
- Blight, K. J., A. A. Kolykhalov, and C. M. Rice. 2000. Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290:1972-1974. - PubMed
-
- Borgatti, P., G. Zauli, M. L. Colamussi, D. Gibellini, M. Previati, L. L. Cantley, and S. Capitani. 1997. Extracellular HIV-1 Tat protein activates phosphatidylinositol 3- and Akt/PKB kinases in CD4+ T lymphoblastoid Jurkat cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 27:2805-2811. - PubMed
-
- Brown, J. P., D. R. Twardzik, H. Marquardt, and G. J. Todaro. 1985. Vaccinia virus encodes a polypeptide homologous to epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor. Nature 313:491-492. - PubMed
-
- Cantrell, D. A. 2001. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling pathways. J. Cell Sci. 114:1439-1445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

