Potent and specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by RNA interference
- PMID: 12186906
- PMCID: PMC136455
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9225-9231.2002
Potent and specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by RNA interference
Abstract
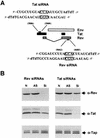
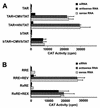
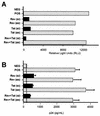
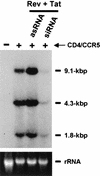
Synthetic small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) have been shown to induce the degradation of specific mRNA targets in human cells by inducing RNA interference (RNAi). Here, we demonstrate that siRNA duplexes targeted against the essential Tat and Rev regulatory proteins encoded by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) can specifically block Tat and Rev expression and function. More importantly, we show that these same siRNAs can effectively inhibit HIV-1 gene expression and replication in cell cultures, including those of human T-cell lines and primary lymphocytes. These observations demonstrate that RNAi can effectively block virus replication in human cells and raise the possibility that RNAi could provide an important innate protective response, particularly against viruses that express double-stranded RNAs as part of their replication cycle.
Figures


References
-
- Ancellin, N., C. Colmont, J. Su, Q. Li, N. Mittereder, S. S. Chae, S. Steffansson, G. Liau, and T. Hla.2002. Extracellular export of sphingosine kinase-1 enzyme. Sphingosine 1-phosphate generation and the induction of angiogenic vascular maturation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:6667-6675. - PubMed
-
- Arts, E. J., M. E. Quiñones-Mateu, J. L. Albright, J.-P. Marois, C. Hough, Z. Gu, and M. A. Wainberg.1998. 3′-Azido-3′-deoxythymidine (AZT) mediates cross-resistance to nucleoside analogs in the case of AZT-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants. J. Virol. 72:4858-4865. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baltimore, D.1988. Intracellular immunization. Nature 335:395-396. - PubMed
-
- Bogerd, H. P., A. Echarri, T. M. Ross, and B. R. Cullen.1998. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus Rev and human T-cell leukemia virus Rex function, but not Mason-Pfizer monkey virus constitutive transport element activity, by a mutant human nucleoporin targeted to Crm1. J. Virol. 72:8627-8635. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

