Potential role of endocrine gastrin in the colonic adenoma carcinoma sequence
- PMID: 12189558
- PMCID: PMC2376163
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600509
Potential role of endocrine gastrin in the colonic adenoma carcinoma sequence
Abstract
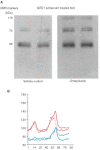
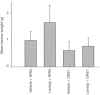
The role of hyper-gastrinaemia in the incidence of colonic cancer remains to be clarified. The aim of this study was to determine whether cholecystokinin-2 (CCK-2) receptor expression predicts the sensitivity of human colonic adenomas to the proliferative effects of serum hyper-gastrinaemia. Gene expression of the classical (74 kDa) CCK-2 receptor in human colonic adenoma specimens and cell lines, was quantified by real-time PCR. Western blotting, using a CCK-2 receptor antiserum, confirmed protein expression. A transformed human colonic adenoma was grown in SCID mice, with hyper-gastrinaemia induced by proton pump inhibitors. CCK-2 receptor blockade was achieved by using neutralising antiserum. Both human colonic adenoma cell lines and biopsies expressed CCK-2 receptor mRNA at levels comparable with CCK-2 receptor transfected fibroblasts and oxyntic mucosa. Western blotting confirmed immunoreactive CCK-2 receptor bands localised to 45, 74 and 82.5 kDa. Omeprazole and lansoprazole-induced hyper-gastrinaemia (resulting in serum gastrin levels of 34.0 and 153.0 pM, respectively) significantly increased the weight of the human adenoma grafts (43% (P=0.016) and 70% (P=0.014), respectively). The effect of hypergastrinaemia on tumour growth was reversed by use of antiserum directed against the CCK-2 receptor. Hyper-gastrinaemia may promote proliferation of human colonic adenomas that express CCK-2 receptor isoforms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential expression of gastrin, cholecystokinin-A and cholecystokinin-B receptor mRNA in human pancreatic cancer cell lines.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jul;36(7):738-43. doi: 10.1080/003655201300192003. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11444473
-
Hypergastrinemia promotes adenoma progression in the APC(Min-/+) mouse model of familial adenomatous polyposis.Cancer Res. 2001 Jan 15;61(2):625-31. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11212260
-
Endogenous hypergastrinaemia does not promote growth of colonic mucosa or of a transplanted colon adenocarcinoma in rats.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Apr;10(4):293-9. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199804000-00004. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998. PMID: 9855044
-
Gastric phenotypic abnormality in cholecystokinin 2 receptor null mice.Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002 Dec;91(6):375-81. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0773.2002.910616.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12688382 Review.
-
The role of gastrin and cholecystokinin in normal and neoplastic gastrointestinal growth.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995 Mar-Apr;10(2):215-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1995.tb01083.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995. PMID: 7787172 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging hazard effects of proton pump inhibitor on the risk of colorectal cancer in low-risk populations: A Korean nationwide prospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 7;12(12):e0189114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189114. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29216279 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Proton Pump Inhibitor and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Observational Studies.Korean J Fam Med. 2012 Sep;33(5):272-9. doi: 10.4082/kjfm.2012.33.5.272. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Korean J Fam Med. 2012. PMID: 23115701 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus protein BMRF1 activates gastrin transcription.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(2):745-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.2.745-755.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15613302 Free PMC article.
-
Association of proton pump inhibitors with gastric and colorectal cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1129948. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1129948. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37007006 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of gastrin 17 on beta-catenin/Tcf-4 pathway in Colo320WT colon cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec 14;12(46):7482-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7482. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17167838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breuer-KatschinskiBNemesKMarrARumpBLeiendeckerBBreuerNGoebellH1999. Colorectal Adenoma Study GroupHelicobacter pylori and the risk of colonic adenomas Digestion 60210215 - PubMed
-
- ClarkePAGrimesSMcWilliamsDFKleieWVKhanKMichaeliDCaplinMWatsonSA2001Antibodies directed against retained Intron 4 of the constitutively active CCK-2 receptor bind to a tumour-specific epitope Gastroenterol 1202526
-
- ClarkePAWatsonSA1999Expression of CCKB/Gastrin receptor isoforms in human gastro-intestinal tissue Digestion 60P-40
-
- ClercPLeung-Theung-LongSWangTCDockrayGJBouissonMDelisleMBVaysseNPradayrolLFourmyDDufresneM2002Expression of CCK2 receptors in the murine pancreas: proliferation, transdifferentiation of acinar cells, and neoplasia Gastroenterol 1222428437 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

