Mechanism of rapid transcriptional induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha-responsive genes by NF-kappaB
- PMID: 12192035
- PMCID: PMC135646
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.18.6354-6362.2002
Mechanism of rapid transcriptional induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha-responsive genes by NF-kappaB
Abstract
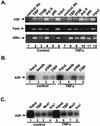
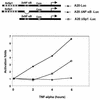
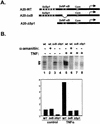
NF-kappaB induces the expression of genes involved in immune response, apoptosis, inflammation, and the cell cycle. Certain NF-kappaB-responsive genes are activated rapidly after the cell is stimulated by cytokines and other extracellular signals. However, the mechanism by which these genes are activated is not entirely understood. Here we report that even though NF-kappaB interacts directly with TAF(II)s, induction of NF-kappaB by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) does not enhance TFIID recruitment and preinitiation complex formation on some NF-kappaB-responsive promoters. These promoters are bound by the transcription apparatus prior to TNF-alpha stimulus. Using the immediate-early TNF-alpha-responsive gene A20 as a prototype promoter, we found that the constitutive association of the general transcription apparatus is mediated by Sp1 and that this is crucial for rapid transcriptional induction by NF-kappaB. In vitro transcription assays confirmed that NF-kappaB plays a postinitiation role since it enhances the transcription reinitiation rate whereas Sp1 is required for the initiation step. Thus, the consecutive effects of Sp1 and NF-kappaB on the transcription process underlie the mechanism of their synergy and allow rapid transcriptional induction in response to cytokines.
Figures
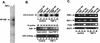



References
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 103:667-678. - PubMed
-
- Albright, S. R., and R. Tjian. 2000. TAFs revisited: more data reveal new twists and confirm old ideas. Gene 242:1-13. - PubMed
-
- Berk, A. J. 1999. Activation of RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11:330-335. - PubMed
-
- Carey, M., Y. S. Lin, M. R. Green, and M. Ptashne. 1990. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature 345:361-364. - PubMed
-
- Dikstein, R., S. Zhou, and R. Tjian. 1996. Human TAFII105 is a cell type-specific TFIID subunit related to hTAFII130. Cell 87:137-146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
