Novel translational control through an iron-responsive element by interaction of multifunctional protein YB-1 and IRP2
- PMID: 12192037
- PMCID: PMC135634
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.18.6375-6383.2002
Novel translational control through an iron-responsive element by interaction of multifunctional protein YB-1 and IRP2
Abstract
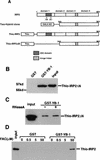
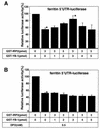
The eukaryotic Y-box-binding protein YB-1 functions in various biological processes, including DNA repair, cell proliferation, and transcriptional and translational controls. To gain further insight into how human YB-1 plays its role in pleiotropic functions, we here used two-hybrid screenings to identify partners of this protein; the results showed that YB-1 itself, iron-regulatory protein 2 (IRP2), and five ribosomal proteins each served as partners to YB-1. We then examined the biological effect of the interaction of YB-1 and IRP2 on translational regulation. Both in vitro binding and coimmunoprecipitation assays showed the direct interaction of YB-1 and IRP2 in the presence of a high concentration of iron. RNA gel shift assays showed that YB-1 reduced the formation of the IRP2-mRNA complex when the iron-responsive element of the ferritin mRNA 5' untranslated region (UTR) was used as a probe. By using an in vitro translation assay using luciferase mRNA ligated to the ferritin mRNA 5'UTR as a reporter construct, we showed that both YB-1 and IRP2 inhibited the translation of the mRNA. However, coadministration of YB-1 and IRP2 proteins abrogated the inhibition of protein synthesis by each protein. An In vivo coimmunoprecipitation assay showed that IRP2 bound to YB-1 in the presence of iron and a proteasome inhibitor. The direct interaction of YB-1 and IRP2 provides the first evidence of the involvement of YB-1 in the translational regulation of an iron-related protein.
Figures






References
-
- Chansky, H. A., M. Hu, D. D. Hickstein, and L. Yang. 2001. Oncogenic TLS/ERG and EWS/Fli-1 fusion proteins inhibit RNA splicing mediated by YB-1 protein. Cancer Res. 61:3586-3590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
