Hydrogen/deuterium exchange and mass spectrometric analysis of a protein containing multiple disulfide bonds: Solution structure of recombinant macrophage colony stimulating factor-beta (rhM-CSFbeta)
- PMID: 12192067
- PMCID: PMC2373587
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0204402
Hydrogen/deuterium exchange and mass spectrometric analysis of a protein containing multiple disulfide bonds: Solution structure of recombinant macrophage colony stimulating factor-beta (rhM-CSFbeta)
Abstract
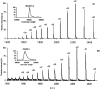
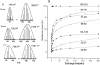
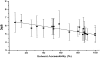
Studies with the homodimeric recombinant human macrophage colony-stimulating factor beta (rhM-CSFbeta), show for the first time that a large number (9) of disulfide linkages can be reduced after amide hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) exchange, and the protein digested and analyzed successfully for the isotopic composition by electrospray mass spectrometry. Analysis of amide H/D after exchange-in shows that in solution the conserved four-helix bundle of (rhM-CSFbeta) has fast and moderately fast exchangeable sections of amide hydrogens in the alphaA helix, and mostly slow exchanging sections of amide hydrogens in the alphaB, alphaC, and alphaD helices. Most of the amide hydrogens in the loop between the beta1 and beta4 sheets exhibited fast or moderately fast exchange, whereas in the amino acid 63-67 loop, located at the interface of the two subunits, the exchange was slow. Solvent accessibility as measured by H/D exchange showed a better correlation with the average depth of amide residues calculated from reported X-ray crystallographic data for rhM-CSFalpha than with the average B-factor. The rates of H/D exchange in rhM-CSFbeta appear to correlate well with the exposed surface calculated for each amino acid residue in the crystal structure except for the alphaD helix. Fast hydrogen isotope exchange throughout the segment amino acids 150-221 present in rhM-CSFbeta, but not rhM-CSFalpha, provides evidence that the carboxy-terminal region is unstructured. It is, therefore, proposed that the anomalous behavior of the alphaD helix is due to interaction of the carboxy-terminal tail with this helical segment.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structural comparison of recombinant human macrophage colony stimulating factor beta and a partially reduced derivative using hydrogen deuterium exchange and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.Protein Sci. 2001 Nov;10(11):2336-45. doi: 10.1110/ps.16701. Protein Sci. 2001. PMID: 11604539 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational analysis of intermediates involved in the in vitro folding pathways of recombinant human macrophage colony stimulating factor beta by sulfhydryl group trapping and hydrogen/deuterium pulsed labeling.Biochemistry. 2002 Dec 31;41(52):15495-504. doi: 10.1021/bi0203841. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12501178
-
Amide hydrogen exchange determined by mass spectrometry: application to rabbit muscle aldolase.Biochemistry. 1996 Jan 23;35(3):779-91. doi: 10.1021/bi952227q. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8547258
-
Measuring the hydrogen/deuterium exchange of proteins at high spatial resolution by mass spectrometry: overcoming gas-phase hydrogen/deuterium scrambling.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Oct 21;47(10):3018-27. doi: 10.1021/ar500194w. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25171396 Review.
-
Insights into enzyme structure and dynamics elucidated by amide H/D exchange mass spectrometry.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 1;433(1):34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.002. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581564 Review.
Cited by
-
Solvent accessibility of betaB2-crystallin and local structural changes due to deamidation at the dimer interface.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Sep;91(3):336-46. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.05.019. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20639133 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of group IA phospholipase A2 with metal ions and phospholipid vesicles probed with deuterium exchange mass spectrometry.Biochemistry. 2008 Jun 17;47(24):6451-9. doi: 10.1021/bi8000962. Epub 2008 May 24. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18500818 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct interaction modes of an AKAP bound to two regulatory subunit isoforms of protein kinase A revealed by amide hydrogen/deuterium exchange.Protein Sci. 2005 Dec;14(12):2982-92. doi: 10.1110/ps.051687305. Epub 2005 Oct 31. Protein Sci. 2005. PMID: 16260760 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational studies of the robust 2-Cys peroxiredoxin Salmonella typhimurium AhpC by solution phase hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) exchange monitored by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.Int J Mass Spectrom. 2011 Apr 30;302(1-3):93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2010.08.018. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21516234 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping surface accessibility of the C1r/C1s tetramer by chemical modification and mass spectrometry provides new insights into assembly of the human C1 complex.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):32251-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149112. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20592021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakravarty, S. and Varadarajan, R. 1999. Residue depth: a novel parameter for the analysis of protein structure and stability. Structure 7 723–732. - PubMed
-
- Clarke, J. and Itzhaki, L.S. 1998. Hydrogen exchange and protein folding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8 112–118. - PubMed
-
- Connolly, M. L. 1983. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science 221 709–13. - PubMed
-
- Das, S.K. and Stanley, E.R. 1982. Structure–function studies of a colony stimulating factor (CSF-1). J. Biol. Chem. 257 13679–13684. - PubMed
-
- Deng, Y., Pan, H., and Smith, D.L. 1999. Selective isotope labeling demonstrates that hydrogen exchange at individual peptide amide linkages can be determined by collision-induced dissociation mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121 1966–1967.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

