Dynamic pattern of reg-2 expression in rat sensory neurons after peripheral nerve injury
- PMID: 12196572
- PMCID: PMC6757959
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-17-07493.2002
Dynamic pattern of reg-2 expression in rat sensory neurons after peripheral nerve injury
Abstract
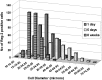
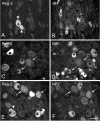
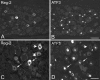
The 16 kDa pancreatitis-associated protein Reg-2 has recently been shown to facilitate the regeneration of motor and sensory neurons after peripheral nerve injury in the adult rat. Reg-2 has also been shown to be a neurotrophic factor that is an essential intermediate in the pathways through which CNTF supports the survival of motor neurons during development. Here we report the dynamic expression of Reg-2 in rat sensory neurons after peripheral nerve injury. Reg-2 is normally not expressed by dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells, but we show, using immunocytochemistry, that Reg-2 is rapidly upregulated in DRG cells after sciatic nerve transection and after 24 hr recovery is expressed almost exclusively in small-diameter neurons that bind the lectin Griffonia simplicifolia IB4 and express the purinoceptor P2X3. However, by 7 d after axotomy, Reg-2 is expressed in medium to large neurons and coexists partly with the neuropeptides galanin and neuropeptide Y, which are also upregulated after peripheral nerve transection. At this time point, Reg-2 is no longer expressed in small neurons, and there is no colocalization with IB4 binding neurons, demonstrating a shift in Reg-2 expression from one subset of DRG neurons to another. We also show by double labeling for activating transcription factor 3, a transcription factor that is upregulated after nerve injury, that Reg-2 expression occurs predominantly in axotomized DRG cells but that a small percentage of uninjured DRG cells also upregulate Reg-2. The selective expression within IB4/P2X3 cells, and the dynamic shift from small to large cells, is unique among DRG peptides and suggests that Reg-2 has a distinctive role in the injury response.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and -2 in dorsal root ganglion neurons after peripheral nerve injury.Neuroscience. 2005;132(1):183-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.003. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15780477
-
Effect of peripheral nerve injury on dorsal root ganglion neurons in the C57 BL/6J mouse: marked changes both in cell numbers and neuropeptide expression.Neuroscience. 2001;105(1):249-63. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00148-8. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11483316
-
Dynamic changes in Robo2 and Slit1 expression in adult rat dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve after peripheral and central axonal injury.Neurosci Res. 2006 Nov;56(3):314-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2006.07.014. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16979769
-
Behavioral models of pain states evoked by physical injury to the peripheral nerve.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Oct;6(4):609-19. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.07.007. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19789066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nerve trauma-caused downregulation of opioid receptors in primary afferent neurons: Molecular mechanisms and potential managements.Exp Neurol. 2021 Mar;337:113572. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113572. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33340498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Essential role of monocytes and macrophages in the progression of acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug 28;16(32):3995-4002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.3995. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20731012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of pancreatitis-associated protein after traumatic brain injury: a mechanism potentially contributing to neuroprotection in human brain.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Nov;31(8):1141-9. doi: 10.1007/s10571-011-9715-0. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21643999 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal cleaved pancreatitis-associated protein-III (PAP-III) serves as a scaffold for neurites and promotes neurite outgrowth.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10205-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.395301. Epub 2013 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23426365 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling and Ingenuity biological function analyses of interleukin-6- versus nerve growth factor-stimulated PC12 cells.BMC Genomics. 2009 Feb 24;10:90. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-90. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19239705 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Reg3β/macrophage TNF-α-mediated positive feedback signaling contributes to pain chronicity in a rat model of CRPS-I.Sci Adv. 2025 Aug;11(31):eadu4270. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu4270. Epub 2025 Aug 1. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40749060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradbury EJ, Burnstock G, McMahon SB. The expression of P2X3 purinoreceptors in sensory neurons: effects of axotomy and glial-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998;12:256–268. - PubMed
-
- Cheema SS, Richards LJ, Murphy M, Bartlett PF. Leukaemia inhibitory factor rescues motoneurones from axotomy-induced cell death. NeuroReport. 1994;5:989–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
