Regulation of V(D)J recombination: a dominant role for promoter positioning in gene segment accessibility
- PMID: 12196630
- PMCID: PMC129441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.182166699
Regulation of V(D)J recombination: a dominant role for promoter positioning in gene segment accessibility
Abstract
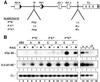
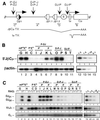
Antigen receptor gene assembly is regulated by transcriptional promoters and enhancers, which control the accessibility of gene segments to a lymphocyte-specific V(D)J recombinase. However, it remained unclear whether accessibility depends on the process of transcription itself or chromatin modifications that accompany transcription. By using T cell receptor beta substrates that integrate stably into nuclear chromatin, we show that promoter location, rather than germ-line transcription or histone acetylation, is a primary determinant of recombination efficiency. These spatial constraints on promoter positioning may reflect an RNA polymerase-independent mechanism to target adjacent gene segments for chromatin remodeling events that facilitate rearrangement.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Promoters, enhancers, and transcription target RAG1 binding during V(D)J recombination.J Exp Med. 2010 Dec 20;207(13):2809-16. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101136. Epub 2010 Nov 29. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 21115692 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of V(D)J recombination by histone acetylation.Curr Biol. 2000 Apr 20;10(8):483-6. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00449-8. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10801420
-
A role for histone acetylation in the developmental regulation of VDJ recombination.Science. 2000 Jan 21;287(5452):495-8. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5452.495. Science. 2000. PMID: 10642553
-
The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination.Cell. 2002 Apr;109 Suppl:S45-55. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00675-x. Cell. 2002. PMID: 11983152 Review.
-
Regulation of antigen receptor gene assembly in lymphocytes.Immunol Res. 2001;23(2-3):121-33. doi: 10.1385/IR:23:2-3:121. Immunol Res. 2001. PMID: 11444378 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of a CTCF-Dependent Insulator on Multiple Aspects of Enhancer-Mediated Chromatin Organization.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;35(20):3504-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00514-15. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26240285 Free PMC article.
-
Pax5 is required for recombination of transcribed, acetylated, 5' IgH V gene segments.Genes Dev. 2003 Jan 1;17(1):37-42. doi: 10.1101/gad.1031403. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12514097 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination may occur in the absence of transcription in the immunoglobulin heavy chain recombination centre.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 17;48(7):3553-3566. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa108. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32086526 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of 12/23-RSS-dependent RAG cleavage by hSWI/SNF complex in the absence of transcription.Mol Cell. 2008 Sep 5;31(5):641-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.012. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18775324 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinogenic effects of DNA-damaging agents are synergistically increased by transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. New insights into transcription-associated recombination.Genetics. 2003 Oct;165(2):457-66. doi: 10.1093/genetics/165.2.457. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 14573461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oettinger M. A., Schatz, D. G., Gorka, C. & Baltimore, D. (1990) Science 248, 1517-1523. - PubMed
-
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger, M. A. & Baltimore, D. (1989) Cell 59, 1036-1048. - PubMed
-
- Hesslein D. G. & Schatz, D. G. (2001) Adv. Immunol. 78, 169-232. - PubMed
-
- Oettinger M. A. (1999) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 325-329. - PubMed
-
- Roth D. B. & Roth, S. Y. (2000) Cell 103, 699-702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

