Long-term serological evaluation of patients with cystic echinococcosis treated with benzimidazole carbamates
- PMID: 12197890
- PMCID: PMC1906476
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01925.x
Long-term serological evaluation of patients with cystic echinococcosis treated with benzimidazole carbamates
Abstract
Seeking better immunological markers indicating the long-term outcome of cystic echinococcosis (CE) after chemotherapy we studied 23 patients receiving albendazole, clinically followed for 8 years, and grouped ultrasonographically according to therapeutic outcome. Antibody responses against a partially purified fraction of hydatid fluid (HFF) and antigen B (AgB) were evaluated by indirect haemagglutination (IHA), ELISA and immunoblotting (IB). Although IHA titres varied over the course of treatment, differences in mean antibody titres to HFF between groups were significant only at 4 years (P = 0.031). IgG isotype expression remained unchanged during follow-up whereas IgE expression decreased in patients with cured or stable disease. AgB disclosed higher IgG4 expression (P < 10(-4); P = 0.025) and lower IgG1 expression than HFF (P < 10(-4); P = 0.022). IHA antibody titres were higher in patients with progressive than in those with cured or stable disease, even in those with the same cyst type. ELISA isotype profiles differed between groups, particularly for type CE 3, 4 and 5 cysts: higher serum IgG1 and IgG3, lower IgG4 and IgE in patients with cured or stable disease. Although combined serological testing provides scarce information on the long-term outcome of CE after chemotherapy it may be useful for reviewing in a retrospective study the outcome of a cyst and for assessing the host-parasite relationship.
Figures
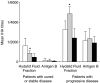
 ) and at the end of follow-up (▪). Student's t-test was used to compare differences between arithmetic means. *P = 0·031
) and at the end of follow-up (▪). Student's t-test was used to compare differences between arithmetic means. *P = 0·031
 ) and at the end of the 8-year follow-up (▪). Student's t-test was used to compare differences between arithmetic means. *P < 10−4; †P = 0·022; ‡P = 0·025. Data represent means ± 2 SD of triplicate experiments.
) and at the end of the 8-year follow-up (▪). Student's t-test was used to compare differences between arithmetic means. *P < 10−4; †P = 0·022; ‡P = 0·025. Data represent means ± 2 SD of triplicate experiments.


References
-
- Pawlowski ZS. Critical points in the clinical management of cystic echinococcosis: a revised review. In: Andersen FL, Ouhelli H, Kachani M, editors. Compendium on Cystic Echinococcosis. Brigham Young University PrintServices: Provo; 1997. pp. 199–235.
-
- Franchi C, Di Vico B, Teggi A. Long-term evaluation of patients with hydatidosis treated with benzimidazole carbamates. Clin Inf Dis. 1999;29:304–9. - PubMed
-
- Wen H, Craig PS. Immunoglobulin G subclass responses in human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;51:741–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

