Systemic treatment with anti-CD40 antibody stimulates Langerhans cell migration from the skin
- PMID: 12197894
- PMCID: PMC1906468
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01909.x
Systemic treatment with anti-CD40 antibody stimulates Langerhans cell migration from the skin
Abstract
Epidermal Langerhans cells (LCs) play a pivotal role in the initiation of cutaneous immune responses. The maturation of LCs and their migration from the skin to the T cell areas of draining lymph nodes are essential for the delivery and presentation of antigen to naïve T cells. CD40, which acts as a costimulatory molecule, is present on LCs and the basal layer of keratinocytes in the skin. We show here that systemic treatment of mice with anti-CD40 antibody stimulates the migration of LCs out of the epidermis with a 70% reduction in LC numbers after 7 days, although changes in LC morphology are detectable as early as day 3. LC numbers in the epidermis returned to 90% of normal by day 21. As well as morphological changes, LC showed up-regulated levels of Class II and ICAM-1, with only minimal changes in CD86 expression 3 days following anti-CD40 treatment. Despite increased levels of Class II and ICAM-1, epidermal LC isolated from anti-CD40 treated mice were poor stimulators of a unidirectional allogeneic mixed leucocyte reaction (MLR), as were epidermal LC isolated from control mice. These results indicate that CD40 stimulation is an effective signal for LC migration, distinct from maturation of immunostimulatory function in the epidermis, which is not altered. These observations may have important implications for the mechanism of action of agonistic anti-CD40 antibodies, which have been used as an adjuvant in models of infection and experimental tumours and the primary immunodeficiency Hyper IgM syndrome caused by deficiency of CD40 ligand.
Figures

 ; anti-CD40. P-values are: *P = 1·6 × 10−11, **P = 2·3 × 10−15. (b) The numbers of LC in the epidermis at days 1, 3, and 7 following a single i.p. injection of 250 μg moAb 1C10 (anti-CD40) are shown. The control moAb, MAC 193, had no effect on LC numbers and the data on days 1, 3 and 7 have been pooled. P-values are: *P = 4 × 10−8, **P = 1·1 × 10−25. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a. (c) Langerhans cells stained with MHC Class II FITC in epidermal sheets of anti-CD40 (3/23) and control moAb (MAC193)-treated mice at days 3, 4 and 7 after a single i.p. injection of 250 μg antibody (original magnification × 200). Increases in the size of LC and MHC Class II expression are seen on days 3 and 4 before effects on LC numbers, which are most marked by day 7. (d) CD40 knockout and 129/Sv wildtype mice were given a single i.p. injection of anti-CD40 antibody (3/23) or control moAb (MAC193) and the numbers of LC counted on day 7. The statistical difference in the LC numbers between the anti-CD40 treated control and CD40 knockout mice is *P = 3·1 × 10−5. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a.
; anti-CD40. P-values are: *P = 1·6 × 10−11, **P = 2·3 × 10−15. (b) The numbers of LC in the epidermis at days 1, 3, and 7 following a single i.p. injection of 250 μg moAb 1C10 (anti-CD40) are shown. The control moAb, MAC 193, had no effect on LC numbers and the data on days 1, 3 and 7 have been pooled. P-values are: *P = 4 × 10−8, **P = 1·1 × 10−25. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a. (c) Langerhans cells stained with MHC Class II FITC in epidermal sheets of anti-CD40 (3/23) and control moAb (MAC193)-treated mice at days 3, 4 and 7 after a single i.p. injection of 250 μg antibody (original magnification × 200). Increases in the size of LC and MHC Class II expression are seen on days 3 and 4 before effects on LC numbers, which are most marked by day 7. (d) CD40 knockout and 129/Sv wildtype mice were given a single i.p. injection of anti-CD40 antibody (3/23) or control moAb (MAC193) and the numbers of LC counted on day 7. The statistical difference in the LC numbers between the anti-CD40 treated control and CD40 knockout mice is *P = 3·1 × 10−5. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a.
 ; anti-CD40. P-values are: *P = 1·6 × 10−11, **P = 2·3 × 10−15. (b) The numbers of LC in the epidermis at days 1, 3, and 7 following a single i.p. injection of 250 μg moAb 1C10 (anti-CD40) are shown. The control moAb, MAC 193, had no effect on LC numbers and the data on days 1, 3 and 7 have been pooled. P-values are: *P = 4 × 10−8, **P = 1·1 × 10−25. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a. (c) Langerhans cells stained with MHC Class II FITC in epidermal sheets of anti-CD40 (3/23) and control moAb (MAC193)-treated mice at days 3, 4 and 7 after a single i.p. injection of 250 μg antibody (original magnification × 200). Increases in the size of LC and MHC Class II expression are seen on days 3 and 4 before effects on LC numbers, which are most marked by day 7. (d) CD40 knockout and 129/Sv wildtype mice were given a single i.p. injection of anti-CD40 antibody (3/23) or control moAb (MAC193) and the numbers of LC counted on day 7. The statistical difference in the LC numbers between the anti-CD40 treated control and CD40 knockout mice is *P = 3·1 × 10−5. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a.
; anti-CD40. P-values are: *P = 1·6 × 10−11, **P = 2·3 × 10−15. (b) The numbers of LC in the epidermis at days 1, 3, and 7 following a single i.p. injection of 250 μg moAb 1C10 (anti-CD40) are shown. The control moAb, MAC 193, had no effect on LC numbers and the data on days 1, 3 and 7 have been pooled. P-values are: *P = 4 × 10−8, **P = 1·1 × 10−25. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a. (c) Langerhans cells stained with MHC Class II FITC in epidermal sheets of anti-CD40 (3/23) and control moAb (MAC193)-treated mice at days 3, 4 and 7 after a single i.p. injection of 250 μg antibody (original magnification × 200). Increases in the size of LC and MHC Class II expression are seen on days 3 and 4 before effects on LC numbers, which are most marked by day 7. (d) CD40 knockout and 129/Sv wildtype mice were given a single i.p. injection of anti-CD40 antibody (3/23) or control moAb (MAC193) and the numbers of LC counted on day 7. The statistical difference in the LC numbers between the anti-CD40 treated control and CD40 knockout mice is *P = 3·1 × 10−5. Results are as described in legend to Fig. 1a.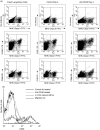

Similar articles
-
Alpha 6 integrins are required for Langerhans cell migration from the epidermis.J Exp Med. 1997 Nov 17;186(10):1725-35. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.10.1725. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9362532 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization and characterization of migratory Langerhans cells in murine skin and lymph nodes by antibodies against Langerin/CD207.J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Feb;120(2):266-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12042.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12542532
-
CD40-CD40 ligand interactions in vivo regulate migration of antigen-bearing dendritic cells from the skin to draining lymph nodes.J Exp Med. 2000 Jun 5;191(11):2011-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.11.2011. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10839815 Free PMC article.
-
Multistep navigation of Langerhans/dendritic cells in and out of the skin.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001 Nov;108(5):688-96. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.118797. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11692090 Review.
-
Functional dichotomy between Langerhans cells that present antigen to naive and to memory/effector T lymphocytes.Immunol Rev. 1990 Oct;117:159-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00572.x. Immunol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2258190 Review.
Cited by
-
Fc-based Duokines: dual-acting costimulatory molecules comprising TNFSF ligands in the single-chain format fused to a heterodimerizing Fc (scDk-Fc).Oncoimmunology. 2022 Jan 20;11(1):2028961. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2028961. eCollection 2022. Oncoimmunology. 2022. PMID: 35083097 Free PMC article.
-
Factors and signals that govern the migration of dendritic cells via lymphatics: recent advances.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005 Jan;26(3):273-87. doi: 10.1007/s00281-004-0168-0. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005. PMID: 15338191 Review.
References
-
- Kimber I, Cumberbatch M, Dearman RJ, Bhushan M, Griffiths CE. Cytokines and chemokines in the initiation and regulation of epidermal Langerhans cell mobilization. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:401–12. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–96. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Bazan F, Blanchard D, et al. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. - PubMed
-
- Turner JG, Rakhmilevich AL, Burdelya L, Neal Z, Imboden M, Sondel PM, Yu H. Anti-CD40 antibody induces antitumor and antimetastatic effects: the role of NK cells. J Immunol. 2001;166:89–94. - PubMed
-
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. Functions of CD40 on B cells, dendritic cells and other cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:330–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

