MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization
- PMID: 12198168
- PMCID: PMC126204
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf476
MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization
Abstract
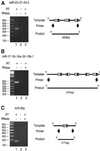
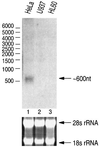
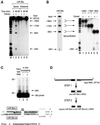
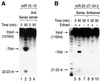
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) constitute a novel, phylogenetically extensive family of small RNAs ( approximately 22 nucleotides) with potential roles in gene regulation. Apart from the finding that miRNAs are produced by Dicer from the precursors of approximately 70 nucleotides (pre-miRNAs), little is known about miRNA biogenesis. Some miRNA genes have been found in close conjunction, suggesting that they are expressed as single transcriptional units. Here, we present in vivo and in vitro evidence that these clustered miRNAs are expressed polycistronically and are processed through at least two sequential steps: (i) generation of the approximately 70 nucleotide pre-miRNAs from the longer transcripts (termed pri-miRNAs); and (ii) processing of pre-miRNAs into mature miRNAs. Subcellular localization studies showed that the first and second steps are compartmentalized into the nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively, and that the pre-miRNA serves as the substrate for nuclear export. Our study suggests that the regulation of miRNA expression may occur at multiple levels, including the two processing steps and the nuclear export step. These data will provide a framework for further studies on miRNA biogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Bernstein E., Caudy,A.A., Hammond,S.M. and Hannon,G.J. (2001) Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature, 409, 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Chang D.D. and Sharp,P.A. (1989) Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell, 59, 789–795. - PubMed
-
- Conti E. and Izaurralde,E. (2001) Nucleocytoplasmic transport enters the atomic age. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 13, 310–319. - PubMed
-
- Dreyfuss G., Kim,V.N. and Kataoka,N. (2002) Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 195–205. - PubMed
-
- Fornerod M., Ohno,M., Yoshida,M. and Mattaj,I.W. (1997) CRM1 is an export receptor for leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Cell, 90, 1051–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

