Interaction of gene-cloned and insect cell-expressed aminopeptidase N of Spodoptera litura with insecticidal crystal protein Cry1C
- PMID: 12200317
- PMCID: PMC124070
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.9.4583-4592.2002
Interaction of gene-cloned and insect cell-expressed aminopeptidase N of Spodoptera litura with insecticidal crystal protein Cry1C
Abstract
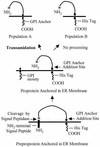
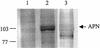
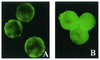
Insecticidal toxins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis interact with specific receptors located in the midguts of susceptible larvae, and the interaction is followed by a series of biochemical events that lead to the death of the insect. In order to elucidate the mechanism of action of B. thuringiensis toxins, receptor protein-encoding genes from many insect species have been cloned and characterized. In this paper we report the cloning, expression, and characterization of Cry toxin-interacting aminopeptidase N (APN) isolated from the midgut of a polyphagous pest, Spodoptera litura. The S. litura APN cDNA was expressed in the Sf21 insect cell line by using a baculovirus expression system. Immunofluorescence staining of the cells revealed that the expressed APN was located at the surface of Sf21 cells. Treatment of Sf21 cells expressing S. litura APN with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C demonstrated that the APN was anchored in the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol moiety. Interaction of the expressed receptor with different Cry toxins was examined by immunofluorescence toxin binding studies and ligand blot and immunoprecipitation analyses. By these experiments we showed that the bioactive toxin, Cry1C, binds to the recombinant APN, while the nonbioactive toxin, Cry1Ac, showed no interaction.
Figures


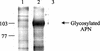


Similar articles
-
Purification and characterization of aminopeptidase N from Spodoptera litura expressed in Sf21 insect cells.Protein Expr Purif. 2007 Aug;54(2):267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2007.03.003. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Protein Expr Purif. 2007. PMID: 17467291
-
Silencing of midgut aminopeptidase N of Spodoptera litura by double-stranded RNA establishes its role as Bacillus thuringiensis toxin receptor.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 6;277(49):46849-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200523200. Epub 2002 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12377776
-
Cloning and characterization of Manduca sexta and Plutella xylostella midgut aminopeptidase N enzymes related to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin-binding proteins.Eur J Biochem. 1997 Sep 15;248(3):748-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00748.x. Eur J Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9342226
-
Cell lines as models for the study of Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Feb;93:66-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.12.008. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29269111 Review.
-
Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Jun;71(2):255-81. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00034-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17554045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aminopeptidase N5 (APN5) as a Putative Functional Receptor of Cry1Ac Toxin in the Larvae of Athetis lepigone.Curr Microbiol. 2017 Apr;74(4):455-459. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1215-0. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Curr Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28224224
-
Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal Cry1ab toxin does not affect the membrane integrity of the mammalian intestinal epithelial cells: An in vitro study.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2006 Jan-Feb;42(1-2):45-9. doi: 10.1007/s11626-006-0011-0. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2006. PMID: 16618212
-
Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein with ribosomal S2 protein triggers larvicidal activity in Spodoptera frugiperda.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Nov;76(21):7202-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01552-10. Epub 2010 Sep 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20833785 Free PMC article.
-
A Spodoptera exigua cadherin serves as a putative receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ca toxin and shows differential enhancement of Cry1Ca and Cry1Ac toxicity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Sep;79(18):5576-83. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01519-13. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23835184 Free PMC article.
-
Cadherin CsCad plays differential functional roles in Cry1Ab and Cry1C intoxication in Chilo suppressalis.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 11;9(1):8507. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44451-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31186483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Chang, W. X. Z., L. J. Gahan, B. E. Tabashnik, and D. G. Heckel. 1999. A new aminopeptidase from diamondback moth provides evidence for a gene duplication event in Lepidoptera. Insect Mol. Biol. 8:171-177. - PubMed
-
- Denolf, P., K. Hendrickx, J. Van Damme, S. Jansens, M. Peferoen, D. Degheele, and J. Van Rie. 1997. Cloning and characterization of M. sexta and P. xylostella midgut aminopeptidase N enzymes related to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin-binding proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 248:748-761. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhaber, B., P. Bork, and F. Eisenhaber. 1999. Prediction of potential GPI-modification sites in proprotein sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 292:741-758. - PubMed
-
- Emmerling, M., D. Chandler, and M. Sandeman. 2001. Molecular cloning of three cDNAs encoding aminopeptidases from the midgut of Helicoverpa punctigera, the Australian native budworm. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 31:899-907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

