Enzymatic degradation of chlorodiamino-s-triazine
- PMID: 12200330
- PMCID: PMC124118
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.9.4672-4675.2002
Enzymatic degradation of chlorodiamino-s-triazine
Abstract
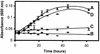
2-Chloro-4,6-diamino-s-triazine (CAAT) is a metabolite of atrazine biodegradation in soils. Atrazine chlorohydrolase (AtzA) catalyzes the dechlorination of atrazine but is unreactive with CAAT. In this study, melamine deaminase (TriA), which is 98% identical to AtzA, catalyzed deamination of CAAT to produce 2-chloro-4-amino-6-hydroxy-s-triazine (CAOT). CAOT underwent dechlorination via hydroxyatrazine ethylaminohydrolase (AtzB) to yield ammelide. This represents a newly discovered dechlorination reaction for AtzB. Ammelide was subsequently hydrolyzed by N-isopropylammelide isopropylaminohydrolase to produce cyanuric acid, a compound metabolized by a variety of soil bacteria.
Figures
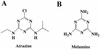
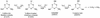
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

