X-linked thrombocytopenia with thalassemia from a mutation in the amino finger of GATA-1 affecting DNA binding rather than FOG-1 interaction
- PMID: 12200364
- PMCID: PMC2808424
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2002-02-0387
X-linked thrombocytopenia with thalassemia from a mutation in the amino finger of GATA-1 affecting DNA binding rather than FOG-1 interaction
Abstract
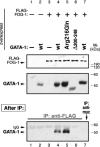
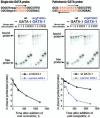
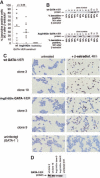
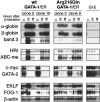
Transcription factor GATA-1 is essential for the development of erythroid cells and megakaryocytes. Each of its 2 zinc fingers is critical for normal function. The C-terminal finger is necessary for DNA binding. The N finger mediates interaction with FOG-1, a cofactor for GATA-1, and also modulates DNA-binding affinity, notably at complex or palindromic GATA sites. Residues of the N finger-mediating interaction with FOG-1 lie on the surface of the N finger facing away from DNA. Strong sequence conservation of residues facing DNA suggests that this other surface may also have an important role. We report here that a syndrome of X-linked thrombocytopenia with thalassemia in humans is caused by a missense mutation (Arg216Gln) in the GATA-1 N finger. To investigate the functional consequences of this substitution, we used site-directed mutagenesis to alter the corresponding residue in GATA-1. Compared with wild-type GATA-1, Arg216Gln GATA-1 shows comparable affinity to single GATA sites but decreased affinity to palindromic sites. Arg216Gln GATA-1 interacts with FOG-1 similarly with wild-type GATA-1. Arg216Gln GATA-1 supports erythroid maturation of GATA-1 erythroid cells, albeit at reduced efficiency compared with wild-type GATA-1. Together, these findings suggest that residues of the N finger of GATA-1-facing DNA contribute to GATA-1 function apart from interaction with the cofactor FOG-1. This is also the first example of beta-thalassemia in humans caused by a mutation in an erythroid transcription factor.
Figures

References
-
- Orkin SH. Embryonic stem cells and transgenic mice in the study of hematopoiesis. Int J Dev Biol. 1998;42:927–934. - PubMed
-
- Vyas P, Ault K, Jackson CW, Orkin SH, Shivdasani RA. Consequences of GATA-1 deficiency in megakaryocytes and platelets. Blood. 1999;93:2867–2875. - PubMed
-
- Lowry JA, Atchley WR. Molecular evolution of the GATA family of transcription factors: conservation within the DNA-binding domain. J Mol Evolution. 2000;50:103–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

