Specific immunotherapy in Albanian patients with anaphylaxis to hymenoptera venoms
- PMID: 12201901
- PMCID: PMC128821
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-5945-2-11
Specific immunotherapy in Albanian patients with anaphylaxis to hymenoptera venoms
Abstract
Background: Severe allergic reactions during rush-specific immunotherapy (Rush-SIT) may occur in the treatment of hymenoptera sting allergy. The objective of the present study was to examine the characteristics of allergic reactions during Rush-SIT in a cohort of patients with allergy towards hymenoptera venom in the mediterranean population of Albania.
Methods: A retrospective study was performed using the clinical reports of 37 patients with venom of bee (apinae), wasp (vespidae, subfamily vespinae) or paperwasp (vespidae, subfamily polistinae) allergy treated with Rush-SIT between 1987 and 1996. After hymenoptera sting allergy diagnosis according to anamnesis and intracutaneous tests the patient were treated with Rush-SIT. The protocol lasted 3 - 4 d with an increase in the concentration from 0.01 microg/ml to 100 microg/ml. Anaphylactic reactions were classified according to the Mueller-classification.
Results: The frequency of reactions during Rush-SIT for bee-venom was 4.7% and for wasp-venom was 1.5% (p < 0.01). The mean frequency of reactions of Mueller grade II for the bee-venom Rush-SIT patients during the first 4 d (= 26 injections) was 0.73 and for the wasp-venom Rush-SIT patients 0.15. No patient experienced a third-degree reaction. 94.6% of the patient supported an end dose of 100 microg.
Conclusions: Rush-SIT is a reliable method for the treatment of anaphylactic reactions to hymenoptera venom even in less developed countries. Bee-venom Rush-SIT was found to cause higher numbers allergic reactions than wasp or paperwasp Rush-SIT.
Figures
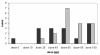
References
-
- Mosbech H. Death caused by wasp and bee stings in Denmark 1960–1980. Allergy. 1983;38:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Barnard JH. Studies of 400 Hymenoptera sting deaths in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973;52:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Georgitis J, Reisman R. Venom skin tests in insect-allergic and insect-nonallergic populations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985;76:803–807. - PubMed
-
- Müller U, Mosbech H, Blaauw P, Dreborg S, Malling H, Przybilla B, Urbanek R, Pastorello E, Blanca M, Bosquet J, Jarisch R, Youlten L. Emergency treatment of allergic reactions to hymenoptera stings. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991;21:281–288. - PubMed
-
- Valentine M, Schuberth K, Sobotka A, Graft D, Kwiterovich K, Szklo M, Lichtenstein L. The value of immunotherapy with venom in children with allergy to insect stings. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1601–1603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

