Determination of novel Borrelia genospecies in Swedish Ixodes ricinus ticks
- PMID: 12202571
- PMCID: PMC130762
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.9.3308-3312.2002
Determination of novel Borrelia genospecies in Swedish Ixodes ricinus ticks
Abstract
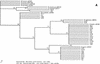
A total of 301 adult questing Ixodes ricinus ticks were collected at 15 different locations along the south and east coasts of Sweden to determine the Borrelia genospecies diversity. Thirty-two ticks (11%) were found to be positive by nested PCR with Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato-specific primers. Species determination was based on partial sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and the flagellin gene. Five different Borrelia species were found. The nucleotide sequence of the Borrelia DNA found in two ticks differed extensively from the nucleotide sequences of the Borrelia DNA found in the other ticks, and analysis revealed that they were closely related to the relapsing fever borrelia species Borrelia miyamotoi. This is the first report of a B. miyamotoi-like borrelia in I. ricinus and in Europe. Moreover, the Borrelia DNA of two ticks (6%) clustered within the B. valaisiana complex. B. valaisiana has not previously been reported in Sweden. B. afzelii DNA was found in 14 ticks (44%), and B. garinii DNA was found in 10 ticks (31%). B. burgdorferi sensu stricto DNA was found in four ticks (13%). We conclude that all of the known human-pathogenic species (B. garinii, B. afzelii, and B. burgdorferi sensu stricto) and B. valaisiana found elsewhere in Europe are also present in the Swedish host-seeking tick population and that a B. miyamotoi-like Borrelia species seems to be present in I. ricinus ticks in Europe.
Figures


References
-
- Anda, P., W. Sánchez-Yebra, M. del Mar Vitutia, E. Rérez Pastrana, I. Rodríguez, N. S. Miller, P. B. Backenson, and J. L. Benach. 1996. A new Borrelia species isolated from patients with relapsing fever in Spain. Lancet 348:162-165. - PubMed
-
- Åsbrink, E., B. Hederstedt, and A. Hovmark. 1984. The spirochetal etiology of erythema chronicum migrans afzelius. Acta Dermatol. Venerol. 64:291-295. - PubMed
-
- Balmelli, T., and J. C. Piffaretti. 1995. Association between different clinical manifestations of Lyme disease and different species of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. Res. Microbiol. 146:329-340. - PubMed
-
- Baranton, G., D. Postic, I. Saint Girons, P. Boerlin, J. C. Piffaretti, M. Assous, and P. A. Grimont. 1992. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS 461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42:378-383. - PubMed
-
- Barbour, A. G., G. O. Maupin, G. J. Teltow, C. J. Carter, and J. Piesman. 1996. Identification of an uncultivable Borrelia species in the hard tick Amblyomma americanum: possible agent of a Lyme disease-like illness. J. Infect. Dis. 173:403-409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

