Malignant catarrhal fever-like disease in Barbary red deer (Cervus elaphus barbarus) naturally infected with a virus resembling alcelaphine herpesvirus 2
- PMID: 12202582
- PMCID: PMC130662
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.9.3381-3390.2002
Malignant catarrhal fever-like disease in Barbary red deer (Cervus elaphus barbarus) naturally infected with a virus resembling alcelaphine herpesvirus 2
Abstract
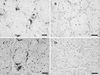
Eight Barbary red deer (Cervus elaphus barbarus) developed clinical signs suggestive of malignant catarrhal fever (MCF) over a 28-day period. These animals were housed outdoors with four other species of ruminants. Affected red deer had lethargy, ocular signs, and nasal discharge and were euthanatized within 48 h. Lesions included ulcers of the muzzle, lips, and oral cavity associated with infiltrates of neutrophils and lymphocytes. Serologically, six of seven red deer tested during the outbreak were positive by competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies to a shared MCF virus antigen. PCR using oligonucleotide primers designed for a conserved protein of alcelaphine herpesviruses 1 (AlHV-1) and 2 (AlHV-2) and for conserved regions of a herpesvirus DNA polymerase gene was positive for tissues from all eight clinically affected animals and negative for eight out of eight red deer without clinical signs of MCF. DNA sequencing of PCR amplicons from the diseased red deer indicated that they were infected with a novel herpesvirus closely related to AlHV-2; immunohistochemistry using polyclonal anti-AlHV-2 serum and in situ hybridization demonstrated the presence of virus within salivary glands adjacent to oral lesions of affected animals. A survey of other ruminants near the outbreak subsequently showed that normal Jackson's hartebeest (Alcelaphus buselaphus jacksoni) that were cohoused with the diseased red deer were infected with the same virus and were shedding the virus in nasal excretions. These findings suggest that a herpesvirus closely related to AlHV-2 caused the MCF-like disease epizootic in Barbary red deer and that the virus may have originated from Jackson's hartebeest.
Figures




References
-
- Baxter, S. I., I. Pow, A. Bridgen, and H. W. Reid. 1993. PCR detection of the sheep-associated agent of malignant catarrhal fever. Arch. Virol. 132:145-159. - PubMed
-
- Blake, J. E., N. O. Nielsen, and W. P. Heuschele. 1990. Lymphoproliferation in captive wild ruminants affected with malignant catarrhal fever: 25 cases (1977-1985). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 196:1141-1143. - PubMed
-
- Brown, C. C., and L. L. Bloss. 1992. An epizootic of malignant catarrhal fever in a large captive herd of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J. Wildl. Dis. 28:301-305. - PubMed
-
- Chmielewicz, B., M. Goltz, and B. Ehlers. 2001. Detection and multigenic characterization of a novel gammaherpesvirus in goats. Virus Res. 75:87-94. - PubMed
-
- Collins, J. K., C. Bruns, T. L. Vermedahl, A. L. Schiebel, M. T. Jessen, P. C. Schultheiss, G. M. Anderson, R. P. Dinsmore, R. J. Callan, and J. C. DeMartini. 2000. Malignant catarrhal fever: polymerase chain reaction survey for ovine herpesvirus 2 and other persistent herpesvirus and retrovirus infections of dairy cattle and bison. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 12:406-411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

