Modulation of cathepsin G expression in severe atopic dermatitis following medium-dose UVA1 phototherapy
- PMID: 12204095
- PMCID: PMC126230
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-5945-2-12
Modulation of cathepsin G expression in severe atopic dermatitis following medium-dose UVA1 phototherapy
Abstract
Background: During the last decade, medium-dose UVA1 phototherapy (50 J/cm2) has achieved great value within the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis (AD). The purpose of our study was to investigate to what extent UVA1 irradiation is able to modulate the status of protease activity by the use of a monoclonal antibody labeling cathepsin G.
Methods: In order to further elucidate the mechanisms by which medium-dose UVA1 irradiation leads to an improvement of skin status in patients with AD, biopsy specimens from 15 patients before and after treatment were analyzed immunohistochemically for proteolytic activation.
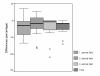
Results: Compared to lesional skin of patients with AD before UVA1 irradiation, the number of cells positive for cathepsin G within the dermal infiltrate decreased significantly after treatment. The decrease of cathepsin G+ cells was closely linked to a substantial clinical improvement in skin condition.
Conclusions: In summary, our findings demonstrated that medium-dose UVA1 irradiation leads to a modulation of the expression of cathepsin G in the dermal inflammatory infiltrate in patients with severe AD. Cathepsin G may attack laminin, proteoglycans, collagen I and insoluble fibronectin, to provoke proinflammatory events, to degrade the basement membrane, to destroy the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and to increase the endothelial permeability. Therefore, its down-regulation by UVA1 phototherapy may induce the reduction of skin inflammation as well as improvement of the skin condition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mononuclear cells in atopic dermatitis in vivo: immunomodulation of the cutaneous infiltrate by medium-dose UVA1 phototherapy.Eur J Med Res. 2002 Jul 24;7(7):315-22. Eur J Med Res. 2002. PMID: 12176681 Clinical Trial.
-
Opposing effects of UVA1 phototherapy on the expression of bcl-2 and p53 in atopic dermatitis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2001 Apr;293(4):178-83. doi: 10.1007/s004030100216. Arch Dermatol Res. 2001. PMID: 11380150
-
Efficacy of ultraviolet A1 phototherapy on the expression of bcl-2 in atopic dermatitis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in vivo: a comparison study.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2002 Oct;18(5):217-22. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0781.2002.02740.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2002. PMID: 12390661
-
Treatment regimens, protocols, dosage, and indications for UVA1 phototherapy: facts and controversies.Clin Dermatol. 2013 Jul-Aug;31(4):438-454. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.011. Clin Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23806161 Review.
-
Phototherapy for atopic dermatitis.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015 Jan-Feb;81(1):10-5. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.148557. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015. PMID: 25566890 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophils in Inflammatory Diseases: Unraveling the Impact of Their Derived Molecules and Heterogeneity.Cells. 2023 Nov 13;12(22):2621. doi: 10.3390/cells12222621. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential expression of chemokine and matrix re-modelling genes is associated with contrasting schistosome-induced hepatopathology in murine models.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011 Jun;5(6):e1178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001178. Epub 2011 Jun 7. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011. PMID: 21666794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leung DYM. The skin as a window into the pathogenesis of chronic allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96:302–319. - PubMed
-
- Rothe MJ, Grant-Kels JM. Atopic dermatitis: An update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Kowalzick L, Kleinheinz A, Weichenthal M, et al. Low dose versus medium dose UV-A1 treatment in severe atopic eczema. Acta Derm Venereol. 1995;75:43–45. - PubMed
-
- von Kobyletzki G, Freitag M, Herde M, et al. Phototherapy of severe atopic dermatitis: Comparison between conventional UVA1 phototherapy, UVA1. cold light phototherapy and combined UVA-UVB phototherapy. Hautarzt. 1999;50:27–33. - PubMed
-
- Krutmann J, Czech W, Diepgen T, et al. High-dose UVA1 therapy in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:225–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

