Modulation of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific immune response by using efavirenz, nelfinavir, and stavudine in a rescue therapy regimen for HIV-infected, drug-experienced patients
- PMID: 12204968
- PMCID: PMC120079
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.9.5.1114-1118.2002
Modulation of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific immune response by using efavirenz, nelfinavir, and stavudine in a rescue therapy regimen for HIV-infected, drug-experienced patients
Abstract
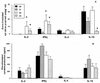
Analysis of the virologic and immunomodulatory effects of an association of efavirenz (EFV), nelfinavir (NFV), and stavudine (d4T) was performed in 18 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected and highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)-experienced patients who failed multiple therapeutic protocols. Patients (<500 CD4(+) cells/ micro l; >10,000 HIV copies/ml) were nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)-naive and were treated for 10 months with EFV (600 mg/day) in association with NFV (750 mg three times daily) and d4T (30 or 40 mg twice daily). Measurement of HIV peptide- and mitogen-stimulated production of interleukin-2 (IL-2), gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), IL-4, and IL-10 as well as quantitation of mRNA for the same cytokines in unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells were performed at baseline and 2 weeks (t1), 2 months (t2), and 10 months (t3) into therapy. The results showed that HIV-specific (but not mitogen-stimulated) IL-2 and IFN-gamma production was augmented and IL-10 production was reduced in patients who received EFV, NFV, and d4T. Therapy was also associated with a reduction in HIV RNA in plasma and an increase in CD4(+) cell count. These changes occurred in the first year of therapy (t2 and t3) and were confirmed by quantitation of cytokine-specific mRNA. Therapy with EFV, NFV, and d4T increases HIV-specific type 1 cytokine production as well as CD4 counts and reduces plasma viremia. This therapeutic regimen may be considered for use in cases of advanced HIV infection.
Figures

References
-
- Angel, J. A. B., K. G. Parato, A. Kumar, S. Kravcik, A. D. Badley, C. Fex, D. Ashby, E. Sun, and D. W. Cameron. 2001. Progressive human immunodeficiency virus-specific immune recovery with prolonged viral suppression. J. Infect. Dis. 185:546-554. - PubMed
-
- Angel, J. A. B., A. Kumar, A. Parato, L. G. Filion, F. Diaz-Mitoma, P. Daftarian, B. Pham, E. Sun, J. M. Leonard, and D. W. Cameron. 1998. Improvement in cell-mediated immune function during potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus therapy with ritonavir plus saquinavir. J. Infect. Dis. 177:898-904. - PubMed
-
- Autran, B., G. Carcelain, T. S. Li, C. Blanc, D. Mathez, R. Tubiana, C. Katlama, P. Debre, and J. Leibowitch. 1997. Positive effects of combined antiretroviral therapy on CD4+ T cell homeostasis and function in advanced HIV disease. Science 277:112-116. - PubMed
-
- Autran, B., and G. Carcelain. 2000. Boosting the immunity to HIV. Can the virus help? Science 290:946-949. - PubMed
-
- Blankson, J. N., J. E. Gallant, and R. F. Siliciano. 2001. Proliferative responses to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antigens in HIV-1-infected patients with immune reconstitution. J. Infect. Dis. 183:657-661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

