CD4(+) CD25(+) T-cell production in healthy humans and in patients with thymic hypoplasia
- PMID: 12204972
- PMCID: PMC120063
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.9.5.1129-1131.2002
CD4(+) CD25(+) T-cell production in healthy humans and in patients with thymic hypoplasia
Abstract
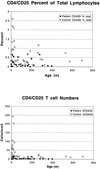
Regulatory T cells are found primarily in the CD4(+) CD25(+) fraction of T cells and play an important role in the prevention of autoimmunity. We examined CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells in 33 healthy children and adults and compared them to a population with an inherited form of thymic hypoplasia and a predisposition to autoimmune disease. Absolute numbers of CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells were markedly higher in healthy infants than in infants with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Baecher-Allan, C., J. A. Brown, G. J. Freeman, et al. 2001. CD4+CD25high regulatory cells in human peripheral blood. J. Immunol. 167:1245-1253. - PubMed
-
- Jawad, A. F., D. M. McDonald-McGinn, E. Zackai, et al. 2001. Immunologic features of chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). J. Pediatr. 139:715-723. - PubMed
-
- Jordan, M. S., A. Boesteanu, A. J. Reed, et al. 2001. Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat. Immunol. 2:301-306. - PubMed
-
- Maloy, K. J., and F. Powrie. 2001. Regulatory T cells in the control of immune pathology. Nat. Immunol. 2:816-822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials