Effects of leptin on cat intestinal vagal mechanoreceptors
- PMID: 12205199
- PMCID: PMC2290517
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.021857
Effects of leptin on cat intestinal vagal mechanoreceptors
Abstract
Vagal afferent nerve fibres are involved in the transmission to the central nervous system of information relating to food intake and immune reactions. Leptin is involved in the control of food intake and has specific receptors in afferent vagal neurones. To investigate the role of these receptors, we studied the effects of leptin on single vagal afferent activities from intestinal mechanoreceptors in anaesthetized cats. The activity of 35 intestinal vagal mechanoreceptors was recorded by means of glass microelectrodes implanted in the nodose ganglion. Leptin (10 microg), administered into the artery irrigating the upper part of the intestine, induced activation in 17 units (P < 0.001), inhibition in 8 units (P < 0.05), and had no effect on 10 units. The excitatory effects of leptin were blocked by the endogenous interleukine-1beta receptor antagonist, (Il-1ra, 250 microg, I.A.). Cholecystokinin (CCK, 10 microg, I.A.) induced an activatory response only in the two types of units which were responsive to leptin alone. When leptin was administered after CCK, its excitatory effects were enhanced and its inhibitory effects were blocked, whereas it had no effect on the units which were not affected by leptin alone. The interactions between leptin and CCK are specific ones, since other substances (phenylbiguanide, a serotoninergic agonist; substance P) known to activate the mechanoreceptors did not modify the effects of leptin. These results indicate that leptin appears to play a role in the control of immune responses and food intake via intestinal vagal afferent nerve fibres and that there is a functional link between leptin and Il-1beta.
Figures
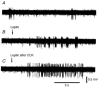



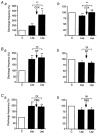
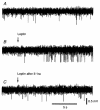


Similar articles
-
Effects of interactions between interleukin-1 beta and leptin on cat intestinal vagal mechanoreceptors.J Physiol. 2004 Feb 15;555(Pt 1):297-310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.054379. Epub 2003 Nov 28. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14645453 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of leptin on cat intestinal motility.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 1;546(Pt 1):267-77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029462. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12509494 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tumor necrosis factor α on leptin-sensitive intestinal vagal mechanoreceptors in the cat.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;91(11):941-50. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2013-0025. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24117262
-
Modulation of vagal afferent excitation and reduction of food intake by leptin and cholecystokinin.Physiol Behav. 2006 Nov 30;89(4):477-85. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.06.017. Epub 2006 Jul 26. Physiol Behav. 2006. PMID: 16872644 Review.
-
Vagal sensory receptors and their reflex effects.Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):159-227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.159. Physiol Rev. 1973. PMID: 4568412 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Examining the Potential Applicability of Orexigenic and Anorexigenic Peptides in Veterinary Medicine for the Management of Obesity in Companion Animals.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 1;46(7):6725-6745. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070401. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin resistance in vagal afferent neurons inhibits cholecystokinin signaling and satiation in diet induced obese rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032967. Epub 2012 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22412960 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory and sympathetic nervous system control of white adipose tissue lipolysis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Apr 29;318(1-2):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.08.031. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19747957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of interactions between interleukin-1 beta and leptin on cat intestinal vagal mechanoreceptors.J Physiol. 2004 Feb 15;555(Pt 1):297-310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.054379. Epub 2003 Nov 28. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14645453 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of leptin on cat intestinal motility.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 1;546(Pt 1):267-77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029462. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12509494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abysique A, Lucchini S, Orsoni P, Mei N, Bouvier M. Effects of alverine citrate on cat intestinal mechanoreceptor responses to chemical and mechanical stimuli. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 1999;13:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Arnalich F, Lopez J, Codoceo R, Jimenez M, Madero R, Montiel C. Relationship of plasma leptin to plasma cytokines and human survival in sepsis and septic shock. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1999;180:908–911. - PubMed
-
- Bado A, Levasseur S, Attoub S, Kermorgant S, Laigneau JP, Bortoluizz MN, Moizo L, Lehy T, Guerre-Millo M, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Lewin MJ. The stomach is a source of leptin. Nature. 1998;394:790–793. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

