Bradykinin potentiation by ACE inhibitors: a matter of metabolism
- PMID: 12208785
- PMCID: PMC1573486
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704862
Bradykinin potentiation by ACE inhibitors: a matter of metabolism
Abstract
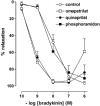
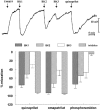
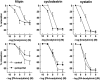
1. Studies in isolated cells overexpressing ACE and bradykinin type 2 (B(2)) receptors suggest that ACE inhibitors potentiate bradykinin by inhibiting B(2) receptor desensitization, via a mechanism involving protein kinase C (PKC) and phosphatases. Here we investigated, in intact porcine coronary arteries, endothelial ACE/B(2) receptor 'crosstalk' as well as bradykinin potentiation through neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibition. 2. NEP inhibition with phosphoramidon did not affect the bradykinin concentration-response curve (CRC), nor did combined NEP/ACE inhibition with omapatrilat exert a further leftward shift on top of the approximately 10 fold leftward shift of the bradykinin CRC observed with ACE inhibition alone. 3. In arteries that, following repeated exposure to 0.1 microM bradykinin, no longer responded to bradykinin ('desensitized' arteries), the ACE inhibitors quinaprilat and angiotensin-(1-7) both induced complete relaxation, without affecting the organ bath fluid levels of bradykinin. This phenomenon was unaffected by inhibition of PKC or phosphatases (with calphostin C and okadaic acid, respectively). 4. When using bradykinin analogues that were either completely or largely ACE-resistant ([Phe(8)psi(CH(2)-NH)Arg(9)]-bradykinin and [deltaPhe(5)]-bradykinin, respectively), the ACE inhibitor-induced shift of the bradykinin CRC was absent, and its ability to reverse desensitization was absent or significantly reduced, respectively. Caveolar disruption with filipin did not affect the quinaprilat-induced effects. Filipin did however reduce the bradykinin-induced relaxation by approximately 25-30%, thereby confirming that B(2) receptor-endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) interaction occurs in caveolae. 5. In conclusion, in porcine arteries, in contrast to transfected cells, bradykinin potentiation by ACE inhibitors is a metabolic process, that can only be explained on the basis of ACE-B(2) receptor co-localization on the endothelial cell membrane. NEP does not appear to affect the bradykinin levels in close proximity to B(2) receptors, and the ACE inhibitor-induced bradykinin potentiation precedes B(2) receptor coupling to eNOS in caveolae.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Bradykinin potentiation by angiotensin-(1-7) and ACE inhibitors correlates with ACE C- and N-domain blockade.Hypertension. 2001 Jul;38(1):95-9. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.38.1.95. Hypertension. 2001. PMID: 11463767
-
Neprilysin inhibitors potentiate effects of bradykinin on b2 receptor.Hypertension. 2002 Feb;39(2 Pt 2):619-23. doi: 10.1161/hy0202.103298. Hypertension. 2002. PMID: 11882619
-
Role of ACE and NEP in bradykinin-induced relaxation and contraction response of isolated porcine basilar artery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002 May;365(5):365-70. doi: 10.1007/s00210-002-0543-0. Epub 2002 Mar 19. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12012022
-
Bradykinin, angiotensin-(1-7), and ACE inhibitors: how do they interact?Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;35(6):792-801. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00273-x. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12676166 Review.
-
Kinins, receptors, kininases and inhibitors--where did they lead us?Biol Chem. 2001 Jan;382(1):43-7. doi: 10.1515/BC.2001.007. Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11258670 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro contractile studies within isolated tissue baths: Translational research from Visible Heart® Laboratories.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Apr;247(7):584-597. doi: 10.1177/15353702211070535. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35068214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and nongenomic effects of aldosterone in the rat heart: why is spironolactone cardioprotective?Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;145(5):664-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706220. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15834444 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of current and prospective antimigraine drugs on the porcine isolated meningeal artery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;374(3):163-75. doi: 10.1007/s00210-006-0108-8. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17103145
-
Heme Oxygenase-1 and Acute Kidney Injury following Cardiac Surgery.Cardiorenal Med. 2014 Apr;4(1):12-21. doi: 10.1159/000357871. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Cardiorenal Med. 2014. PMID: 24847330 Free PMC article.
-
Renin angiotensin system and its role in biomarkers and treatment in gliomas.J Neurooncol. 2018 May;138(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s11060-018-2789-5. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Neurooncol. 2018. PMID: 29450812 Review.
References
-
- BACHVAROV D.R., HOULE S., BACHVAROVA M., BOUTHILLIER J., ADAM A., MARCEAU F. Bradykinin B2 receptor endocytosis, recycling, and down-regulation assessed using green fluorescent protein conjugates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001;297:19–26. - PubMed
-
- BENZING T., FLEMING I., BLAUKAT A., MÜLLER-ESTERL W., BUSSE R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ramiprilat interferes with the sequestration of the B2 kinin receptor within the plasma membrane of native endothelial cells. Circulation. 1999;99:2034–2040. - PubMed
-
- BLAIS C., JR, FORTIN D., ROULEAU J.L., MOLINARO G., ADAM A. Protective effect of omapatrilat, a vasopeptidase inhibitor, on the metabolism of bradykinin in normal and failing human hearts. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000;295:621–626. - PubMed
-
- CAMPBELL D.J., DUNCAN A.M., KLADIS A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition modifies angiotensin but not kinin peptide levels in human atrial tissue. Hypertension. 1999;34:171–175. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

