Human telomerase and its regulation
- PMID: 12208997
- PMCID: PMC120798
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.66.3.407-425.2002
Human telomerase and its regulation
Abstract
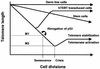
The telomere is a special functional complex at the end of linear eukaryotic chromosomes, consisting of tandem repeat DNA sequences and associated proteins. It is essential for maintaining the integrity and stability of linear eukaryotic genomes. Telomere length regulation and maintenance contribute to normal human cellular aging and human diseases. The synthesis of telomeres is mainly achieved by the cellular reverse transcriptase telomerase, an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase that adds telomeric DNA to telomeres. Expression of telomerase is usually required for cell immortalization and long-term tumor growth. In humans, telomerase activity is tightly regulated during development and oncogenesis. The modulation of telomerase activity may therefore have important implications in antiaging and anticancer therapy. This review describes the currently known components of the telomerase complex and attempts to provide an update on the molecular mechanisms of human telomerase regulation.
Figures


References
-
- Aisner, D. L., W. E. Wright, and J. W. Shay. 2002. Telomerase regulation: not just flipping the switch. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12:80-85. - PubMed
-
- Aldous, W. K., A. J. Marean, M. J. DeHart, L. A. Matej, and K. H. Moore. 1999. Effects of tamoxifen on telomerase activity in breast carcinoma cell lines. Cancer 85:1523-1529. - PubMed
-
- Ancelin, K., M. Brunori, S. Bauwens, C. E. Koering, C. Brun, M. Ricoul, J. P. Pommier, L. Sabatier, and E. Gilson. 2002. Targeting assay to study the cis functions of human telomeric proteins: evidence for inhibition of telomerase by TRF1 and for activation of telomere degradation by TRF2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:3474-3487. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artandi, S. E., and R. A. DePinho. 2000. Mice without telomerase: what can they teach us about human cancer? Nat. Med. 6:852-855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

