GAZE: a generic framework for the integration of gene-prediction data by dynamic programming
- PMID: 12213779
- PMCID: PMC186661
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.149502
GAZE: a generic framework for the integration of gene-prediction data by dynamic programming
Abstract
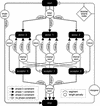
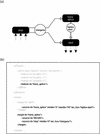
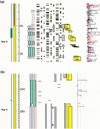
We describe a method (implemented in a program, GAZE) for assembling arbitrary evidence for individual gene components (features) into predictions of complete gene structures. Our system is generic in that both the features themselves, and the model of gene structure against which potential assemblies are validated and scored, are external to the system and supplied by the user. GAZE uses a dynamic programming algorithm to obtain the highest scoring gene structure according to the model and posterior probabilities that each input feature is part of a gene. A novel pruning strategy ensures that the algorithm has a run-time effectively linear in sequence length. To demonstrate the flexibility of our system in the incorporation of additional evidence into the gene prediction process, we show how it can be used to both represent nonstandard gene structures (in the form of trans-spliced genes in Caenorhabditis elegans), and make use of similarity information (in the form of Expressed Sequence Tag alignments), while requiring no change to the underlying software. GAZE is available at http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Software/analysis/GAZE.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Teamed up for transcription.Nature. 2002 Jun 20;417(6891):797-8. doi: 10.1038/417797a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12075329 No abstract available.
-
NemaFootPrinter: a web based software for the identification of conserved non-coding genome sequence regions between C. elegans and C. briggsae.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Dec 1;6 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-S4-S22. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16351749 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNA gene detection using comparative sequence analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2001;2:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-2-8. Epub 2001 Oct 10. BMC Bioinformatics. 2001. PMID: 11801179 Free PMC article.
-
WormBase: methods for data mining and comparative genomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;351:31-50. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-151-7:31. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16988424 Review.
-
RNAi (Nematodes: Caenorhabditis elegans).Adv Genet. 2002;46:339-60. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(02)46012-9. Adv Genet. 2002. PMID: 11931230 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of plant genomes in the FLAGdb++ environment.Plant Methods. 2011 Mar 29;7:8. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-7-8. Plant Methods. 2011. PMID: 21447150 Free PMC article.
-
The rainbow trout genome provides novel insights into evolution after whole-genome duplication in vertebrates.Nat Commun. 2014 Apr 22;5:3657. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4657. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24755649 Free PMC article.
-
Complete DNA sequence of Kuraishia capsulata illustrates novel genomic features among budding yeasts (Saccharomycotina).Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(12):2524-39. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt201. Genome Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 24317973 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing of the smallest Apicomplexan genome from the human pathogen Babesia microti.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(18):9102-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks700. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22833609 Free PMC article.
-
xGDB: open-source computational infrastructure for the integrated evaluation and analysis of genome features.Genome Biol. 2006;7(11):R111. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-11-r111. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 17116260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenthal T, Steward K. RNA processing and gene structure. In: Riddle DL, et al., editors. C. elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. pp. 117–145. - PubMed
-
- Burge C, Karlin S. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J Mol Biol. 1997;268:78–94. - PubMed
-
- Burge C, Karlin S. Finding the genes in genomic DNA. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:346–354. - PubMed
-
- Durbin R, Eddy S, Krogh A, Mitchison G. Biological sequence analysis: Probabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acids (Chapter 3). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1998.
-
- Guigó R. Assembling genes from predicted exons in linear time with dynamic programming. J Comp Biol. 1998;5:681–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
