The gene for juvenile hyaline fibromatosis maps to chromosome 4q21
- PMID: 12214284
- PMCID: PMC378553
- DOI: 10.1086/342776
The gene for juvenile hyaline fibromatosis maps to chromosome 4q21
Abstract
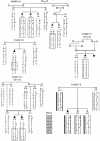
Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis (JHF) is an autosomal recessive condition characterized by multiple subcutaneous nodular tumors, gingival fibromatosis, flexion contractures of the joints, and an accumulation of hyaline in the dermis. We performed a genomewide linkage search in two families with JHF from the same region of the Indian state of Gujarat and identified a region of homozygosity on chromosome 4q21. Dense microsatellite analyses within this interval in five families with JHF who were from diverse origins demonstrate that all are compatible with linkage to chromosome 4q21 (multipoint LOD score 5.5). Meiotic recombinants place the gene for JHF within a 7-cM interval bounded by D4S2393 and D4S395.
Figures


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for identification and order of microsatellite markers)
-
- Ensembl, http://www.ensembl.org/ (for identification of candidate genes)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for JHF [MIM 228600], ISH [MIM 236490], Winchester syndrome [MIM 277950], congenital generalized fibromatosis [MIM 228550], the stiff skin syndrome [MIM 184900], lipoid proteinosis [MIM 247100], pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy [MIM 252600], Farber disease [MIM 228000], and I-cell disease [MIM 252500])
-
- UCSC Genome Bioinformatics, http://genome.cse.ucsc.edu/ (for identification of candidate genes)
References
-
- Allen PW (2001) Selected cases from the Arkadi M Rywlin international slide seminar: hyaline fibromatosis. Adv Anat Pathol 8:173–178 - PubMed
-
- Dunger DB, Dicks-Mireaux C, O’Driscoll P, Lake B, Ersser R, Shaw DG, Grant DB (1987) Two cases of Winchester syndrome with increased urinary oligosaccharide excretion. Eur J Pediatr 146:615–619 - PubMed
-
- Glover MT, Lake BD, Atherton DJ (1991) Infantile systemic hyalinosis: newly recognised disorder of collagen? Pediatrics 87:228–234 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

