The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factor stimulates repair by human excision nuclease in the mononucleosome core particle
- PMID: 12215535
- PMCID: PMC134043
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.19.6779-6787.2002
The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factor stimulates repair by human excision nuclease in the mononucleosome core particle
Abstract
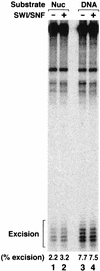
To investigate the role of chromatin remodeling in nucleotide excision repair, we prepared mononucleosomes with a 200-bp duplex containing an acetylaminofluorene-guanine (AAF-G) adduct at a single site. DNase I footprinting revealed a well-phased nucleosome structure with the AAF-G adduct near the center of twofold symmetry of the nucleosome core. This mononucleosome substrate was used to examine the effect of the SWI/SNF remodeling complex on the activity of human excision nuclease reconstituted from six purified excision repair factors. We found that the three repair factors implicated in damage recognition, RPA, XPA, and XPC, stimulate the remodeling activity of SWI/SNF, which in turn stimulates the removal of the AAF-G adduct from the nucleosome core by the excision nuclease. This is the first demonstration of the stimulation of nucleotide excision repair of a lesion in the nucleosome core by a chromatin-remodeling factor and contrasts with the ACF remodeling factor, which stimulates the removal of lesions from internucleosomal linker regions but not from the nucleosome core.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effect of damage type on stimulation of human excision nuclease by SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling factor.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;23(12):4121-5. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4121-4125.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12773556 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage in the nucleosome core is refractory to repair by human excision nuclease.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(24):9173-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9173-9181.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11094069 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of a core chromatin remodeling complex from SWI/SNF subunits.Mol Cell. 1999 Feb;3(2):247-53. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80315-9. Mol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10078207
-
In vitro chromatin templates to study nucleotide excision repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Dec;36:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.09.026. Epub 2015 Oct 22. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 26531320 Review.
-
Three-dimensional structural views of damaged-DNA recognition: T4 endonuclease V, E. coli Vsr protein, and human nucleotide excision repair factor XPA.Mutat Res. 2000 Aug 30;460(3-4):257-75. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00031-8. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10946233 Review.
Cited by
-
Platinum anticancer drug damage enforces a particular rotational setting of DNA in nucleosomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 30;102(35):12311-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506025102. Epub 2005 Aug 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16116097 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of linker histones by DNA-dependent protein kinase is required for DNA ligase IV-dependent ligation in the presence of histone H1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):1877-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401179102. Epub 2005 Jan 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15671175 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin structure and DNA damage repair.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2008 Nov 12;1(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-1-9. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2008. PMID: 19014481 Free PMC article.
-
Monoubiquitinated histone H2A destabilizes photolesion-containing nucleosomes with concomitant release of UV-damaged DNA-binding protein E3 ligase.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 6;287(15):12036-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.307058. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22334663 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide Excision Repair and Impact of Site-Specific 5',8-Cyclopurine and Bulky DNA Lesions on the Physical Properties of Nucleosomes.Biochemistry. 2019 Feb 12;58(6):561-574. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01066. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30570250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aalfs, J. D., and R. E. Kingston. 2000. What does ′chromatin remodeling' mean? Trends Biochem. Sci. 25:548-555. - PubMed
-
- Bessho, T., A. Sancar, L. H. Thompson, and M. P. Thelen. 1997. Reconstitution of human excision nuclease with recombinant XPF-ERCC1 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 272:3833-3837. - PubMed
-
- Branum, M. E., J. T. Reardon, and A. Sancar. 2001. DNA repair excision nuclease attacks undamaged DNA. A potential source of spontaneous mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 276:25421-25426. - PubMed
-
- Fry, C. J., and C. L. Peterson. 2002. Unlocking the gates to gene expression. Science 295:1847-1848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
