Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants
- PMID: 12221975
- PMCID: PMC3128348
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091401.143329
Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants
Abstract
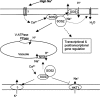
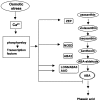
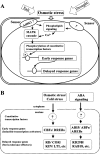
Salt and drought stress signal transduction consists of ionic and osmotic homeostasis signaling pathways, detoxification (i.e., damage control and repair) response pathways, and pathways for growth regulation. The ionic aspect of salt stress is signaled via the SOS pathway where a calcium-responsive SOS3-SOS2 protein kinase complex controls the expression and activity of ion transporters such as SOS1. Osmotic stress activates several protein kinases including mitogen-activated kinases, which may mediate osmotic homeostasis and/or detoxification responses. A number of phospholipid systems are activated by osmotic stress, generating a diverse array of messenger molecules, some of which may function upstream of the osmotic stress-activated protein kinases. Abscisic acid biosynthesis is regulated by osmotic stress at multiple steps. Both ABA-dependent and -independent osmotic stress signaling first modify constitutively expressed transcription factors, leading to the expression of early response transcriptional activators, which then activate downstream stress tolerance effector genes.
Figures



References
-
- Amtmann A, Sanders D. Mechanisms of Na+ uptake by plant cells. Adv. Bot. Res. 1999;29:75–112.
-
- Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+-antiport in Arabidopsis. Science. 1999;285:1256–58. - PubMed
-
- Bastola DR, Pethe VV, Winicov I. Alfin1, a novel zinc-finger protein in alfalfa roots that binds to promoter elements in the salt-inducible MsPRP2 gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998;38:1123–35. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Irvine RF. Inositol phosphate and cell signaling. Nature. 1989;341:197–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

