Chronic morphine induces downregulation of spinal glutamate transporters: implications in morphine tolerance and abnormal pain sensitivity
- PMID: 12223586
- PMCID: PMC6758088
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-08312.2002
Chronic morphine induces downregulation of spinal glutamate transporters: implications in morphine tolerance and abnormal pain sensitivity
Abstract
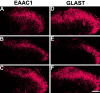
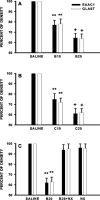
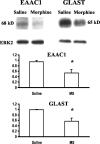
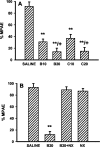
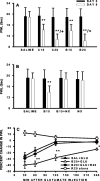
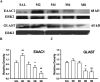
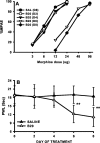
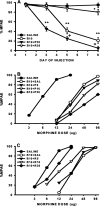
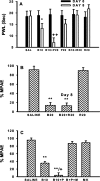
Tolerance to the analgesic effects of an opioid occurs after its chronic administration, a pharmacological phenomenon that has been associated with the development of abnormal pain sensitivity such as hyperalgesia. In the present study, we examined the role of spinal glutamate transporters (GTs) in the development of both morphine tolerance and associated thermal hyperalgesia. Chronic morphine administered through either intrathecal boluses or continuous infusion induced a dose-dependent downregulation of GTs (EAAC1 and GLAST) in the rat's superficial spinal cord dorsal horn. This GT downregulation was mediated through opioid receptors because naloxone blocked such GT changes. Morphine-induced GT downregulation reduced the ability to maintain in vivo glutamate homeostasis at the spinal level, because the hyperalgesic response to exogenous glutamate was enhanced, including an increased magnitude and a prolonged time course, in morphine-treated rats with reduced spinal GTs. Moreover, the downregulation of spinal GTs exhibited a temporal correlation with the development of morphine tolerance and thermal hyperalgesia. Consistently, the GT inhibitor l-trans-pyrrolidine-2-4-dicarboxylate (PDC) potentiated, whereas the positive GT regulator riluzole reduced, the development of both morphine tolerance and thermal hyperalgesia. The effects from regulating spinal GT activity by PDC were at least in part mediated through activation of the NMDA receptor (NMDAR), because the noncompetitive NMDAR antagonist MK-801 blocked both morphine tolerance and thermal hyperalgesia that were potentiated by PDC. These results indicate that spinal GTs may contribute to the neural mechanisms of morphine tolerance and associated abnormal pain sensitivity by means of regulating regional glutamate homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats.J Neurosci. 2003 Apr 1;23(7):2899-910. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02899.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12684477 Free PMC article.
-
N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist d-AP5 prevents pertussis toxin-induced alterations in rat spinal cords by inhibiting increase in concentrations of spinal CSF excitatory amino acids and downregulation of glutamate transporters.Brain Res Bull. 2009 Aug 28;80(1-2):69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.05.004. Epub 2009 May 20. Brain Res Bull. 2009. PMID: 19463918
-
Co-administration of ultra-low dose naloxone attenuates morphine tolerance in rats via attenuation of NMDA receptor neurotransmission and suppression of neuroinflammation in the spinal cords.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010 Aug;96(2):236-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2010.05.012. Epub 2010 May 15. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010. PMID: 20478329
-
Glutamate Transport System as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Chronic Pain: Molecular Mechanisms and Pharmacology.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;16:225-253. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55769-4_11. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28828613 Review.
-
Cellular mechanisms of neuropathic pain, morphine tolerance, and their interactions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jul 6;96(14):7731-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7731. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10393889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting endogenous opioids: Lessons learned from endomorphin 2 in the female rat.Peptides. 2019 Feb;112:133-138. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 30557590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term Morphine-treated Rats are more Sensitive to Antinociceptive Effect of Diclofenac than the Morphine-naive rats.Iran J Pharm Res. 2013 Winter;12(1):175-84. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 24250586 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Blocks Morphine-Induced Place Preference: Involvement of GLT-1, NF-κB, BDNF, and CREB in the Nucleus Accumbens.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Oct 14;15:762297. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.762297. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34720901 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome in drug abuse.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 25;9(6):165-177. eCollection 2017. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29348793 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of the Mechanisms of Opioid Tolerance: Do We Still Say NO?Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jul;41(5):927-948. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01065-8. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33704603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akil H, Mayer DJ. Antagonization of stimulation produced analgesia by p-CPA, a serotonin synthesis inhibitor. Brain Res. 1972;44:692–697. - PubMed
-
- Azbill RD, Mu X, Springer JE. Riluzole increases high-affinity glutamate uptake in rat spinal cord synaptosome. Brain Res. 2000;871:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Bilsky EJ, Bernstein Z, Wang Z, Sadee W, Porreca F. Effects of naloxone and d-Phe-Cys-Tyr-d-Trp-Arg-Thr-Phe-Thr-NH2 and the protein kinase inhibitors H7 and H8 on acute morphine dependence and antinociceptive tolerance in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:484–490. - PubMed
-
- Bohn LM, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainestdinov RR, Peppel K, Caron MG, Lin F. Enhanced morphine analgesia in mice lacking beta-arrestin-2. Science. 1999;286:2495–2498. - PubMed
-
- Bohn LM, Gainestdinov RR, Lin FT, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG. Mu-opioid receptor desensitization by beta-arrestin-2 determines morphine tolerance but not dependence. Nature. 2000;408:720–723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
